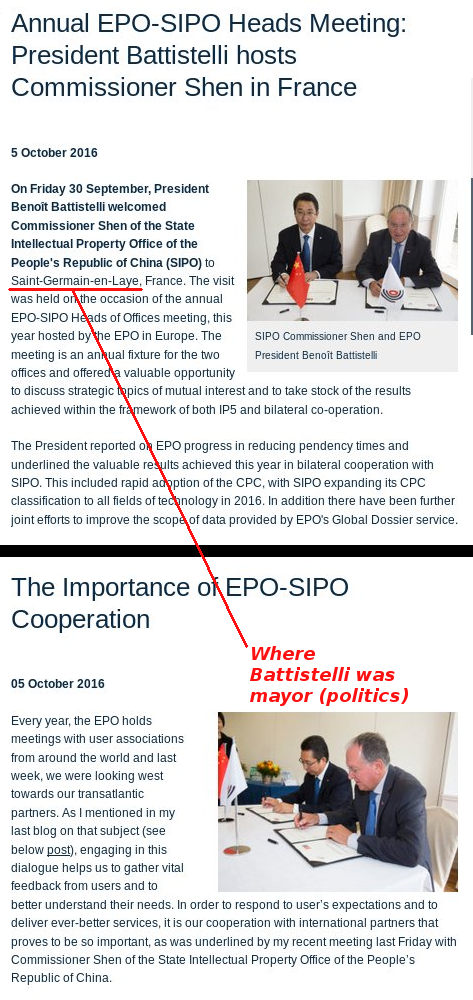
 References: Battistelli and China, 2016 [1, 2, 3]
References: Battistelli and China, 2016 [1, 2, 3]
Summary: This epidemic of the short-sighted mindset wherein more patents are more "success" needs to be ended; but the new President of the EPO shows no signs of deviating from Battistelli's race to the bottom (along with China)
TECHRIGHTS has covered the USPTO more than it has covered the EPO lately. The EPO became very quiet; there are hardly even any tweets or announcements. Like we said earlier this week, the agenda is similar and as we noted yesterday, António Campinos may be just a quieter version of Battistelli. Software patents continue to be granted in Europe and there's no intention to change that under Campinos. It's just patent maximlism all the way.
SIPO is
reorganising, IAM said yesterday, and it also
published this placement which serves to show that TIPO (Taiwan) grants low-quality patents which courts then invalidate. To quote this one example:
Nichia’s invention patent TW156177 relates to a light-emitting diode (LED) comprising a light-emitting component and a phosphor capable of absorbing some of the light emitted, as well as producing light of a different wavelength.
Another thing we covered yesterday is
the belated realisation in China that patent trolling is a real problem. When patent quality is lowered -- as empirical analyses have repeatedly shown -- patent trolls spread.
Yesterday
Patently-O promoted this
recent scholarly paper about patent "Quality vs. Quantity" in China. Composed by Ana Maria Santacreu and Heting Zhu (Federal Reserve Banks - Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis), the abstract says this:
Using three measurements of patent quality, we argue that there is still room for China to improve its innovative activities. Comparing the number of patent applications and patent grants across countries, we see that although the United States and Japan have been global leaders in innovation for a long time, South Korea and China are catching up fast. If China sustains its large innovation investment and shifts its focus from quantity to quality, together with an improvement in intellectual property rights, the likelihood of becoming one of the next innovation leaders could be much higher.
China allows software patents; two years ago it made the rules on this matter even more lenient, which meant that patent quality did not really matter (broadening scope did). China is one of the very few countries in the world that formally permit software patents.
Last night
Managing IP, a site of patent maximlists, published an article titled
"What is driving China's AI patent filing boom?"
"AI" just means "algorithm" these days. The term no longer means what it used to and more often than not it's a loophole for patenting software. The Indian media also did this last night, framing software as “AI” (as in algorithms; plus the hype/buzzword).
This
report from the Times of India soon morphed;
"develops" becomes "patents" in the headline, changing the meaning of the original article.
So going back to the EPO, what is its stance on software patents? Well, it seems like one just need to calls these "ICT", "CII", "AI", "4IR" and so on. Then the EPO is perfectly happy to issue a patent, awarding/granting a monopoly on algorithms.
Mind
this week's press release which celebrates nothing but a patent grant. To quote:
Immuron Limited (ASX:IMC) (NASDAQ:IMRN) is an Australian microbiome biopharmaceutical Company focused on developing and commercializing orally delivered targeted polyclonal antibodies for the treatment of inflammatory mediated and infectious diseases. The Company is pleased to announce that the European Patent Office (EPO) has decided to Grant a patent for the use of a composition for the treatment of Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). This patent (EPO Grant No. 2424890) is entitled “Anti-LPS enriched immunoglobulin preparations for the treatment and/or prophylaxis of a pathologic disorder”). This patent is due to Expire in April 2030, with potential for supplementary protection and extension of this monopoly.
Do they know that the
EPO's patent examination is besieged and many European Patents will later turn out to be bunk? Do they care? Well, they might start caring when their own patents (which they certainly view as "good" and "legitimate") repeatedly perish in courts, costing them millions of euros. Low-quality patent grants cost dearly; both plaintiffs and defendants suffers, but only the lawyers benefit.
⬆

 References: Battistelli and China, 2016 [1, 2, 3]
References: Battistelli and China, 2016 [1, 2, 3]