
Direct/source: 2017 Patent Dispute Report: Year in Review
THE policy at the USPTO notwithstanding (record number of patent grants), courts are unimpressed and patent holders are reluctant to sue. Compare that to China (the very opposite) and Germany, where EPO policy causes a jump in litigation, usually by patent trolls.
"It's good news for productive industries and bad news for parasitic ones."IAM, fed by Watchtroll's latest dishonest nonsense, is not happy. This is a good sign. IAM said this: "Further proof that the anti-patent atmosphere in the US is hitting everyone. Universities have been a life force for American innovation for decades - see the internet, biotech. etc; heck, where did Google come from?"
"These things came into existence IN SPITE of patents," I told IAM, "NOT thanks to them."
It's pretty incredible that IAM, fed by the intellectually-dishonest Watchtroll (written by people who are neither technical nor legal professionals), would claim that the Internet is somehow dependent on patents. The very opposite is true. Google is probably the worst example to use here because Google is often accused of thriving in a landscape of weaker patent policy, not stronger patent policy. Did IAM get bamboozled so easily or is it deliberately spreading falsehoods? Either way, what we see here is a choir of patent maximalists rubbing each other's back. It's an insult to truth itself.
"It grows in the ground, it's part of nature, but humans have found the justification to put patents on it."Sadly, we live in times of "alternative facts". Facts don't receive much respect and truth-tellers haven't much honour. Read this new docket report wherein the 'experts' aren't. To quote: "The court denied defendant's motion for a new trial because defendant was not prejudiced by the court questioning defendant's damages witnesses at trial. "â [Defendant] believes that the Court expressed disdain for its positions in front of the jury, coloring their evaluation of the evidence despite an instruction not to take anything from the Court’s comments during trial. . . .""
They actually tried to demand a new trial over this. They failed.
As we look around the news (this past week) we find a great deal of puff pieces like this one by Lawrence E. Ashery and various articles about the puffing of marijuana [1, 2]. What on Earth does it even have to do with patents? Well, you see, in the US there are even patents related to marijuana. It grows in the ground, it's part of nature, but humans have found the justification to put patents on it. Were they high? Nicole Grimm, Brett Scott, and George "Trey" Lyons, III, who wrote the latter article, call it the "Canna-IP Industry". What on Earth are they smoking? What has patent law come to?
"Patent litigation numbers fell sharply last year. "The worst thing is, in the US it's still possible to get patents on business methods (things one can do with pen and paper) and fairly reasonable court decisions are being described as "much maligned 1978 decision." Maligned by who? And why? The patent maximalists just don't seem to accept the retreat from patent maximalism. It jeopardises their source of income.
Thankfully, whether patent maximalists like it or not, the US is moving away from this 'disease' and according to the latest numbers from Unified Patents:
The Eastern District of Texas accounted for 34% of all new US patent cases pre-TC Heartland in 2017 compared to only 15% post-TC Heartland, according to an analysis by Unified Patents
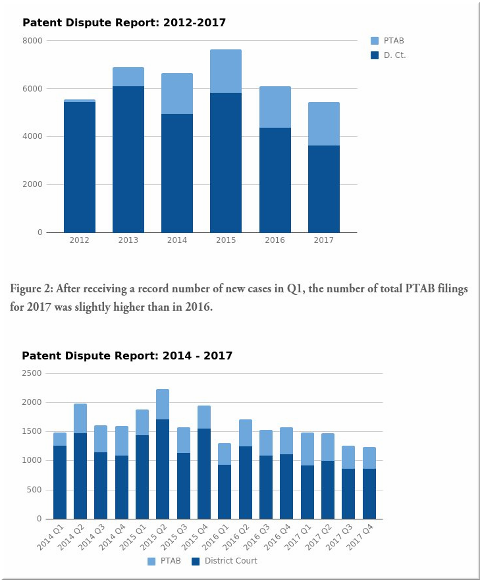
US district court patent litigation dropped 17% to 3,649 new cases in 2017 from 4,382 in 2016, according to a patent dispute report from Unified Patents.
After a big drop in new infringement lawsuits in 2016, last year saw another significant fall as the accumulation of changes to the US patent system over the last decade continue to make the climate particularly challenging for rights owners looking to assert their IP in court. According to Unified Patents the number of new cases fell 17% over the course of the last year - from 4,382 in 2016 to 3,649 in 2017. It was, however, a big year at the PTAB, as a record 1,796 new petitions were filed.
RPX added more context to the litigation numbers with its own review of 2017. According to the defensive aggregator, just over 3,500 defendants were added to new litigation campaigns showing that on a like-for-like basis the number of disputes last year was at a level last seen in 2006. Lex Machina is yet to release its 2017 analysis but the tracker on its platform suggests that the numbers of new cases last year was a little over the 4,000 mark, down from around 4,500 in 2016. Whichever way you cut it, the data points to a very different assertion climate in the world’s largest patent market.