04.30.16
Posted in America, Courtroom, Law, Patents at 7:10 am by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
The US Supreme Court (SCOTUS) has become the target of the profiteers’ anger

Summary: Corporate lobbyists and patent lawyers are trying to put Alice in the grave, for its impact on software patents is very profound and thus far almost unstoppable
THE increasingly-famous decision, commonly known as Alice (the plaintiff), has just claimed another victim. It’s a software patent of course. It’s also a high-profile case (Fitbit and Jawbone) which we covered here several times before (this year and last year).
“The Alice precedence is working. No wonder patent lawyers are in panic.”According to the News Corp.-owned Wall Street Journal (behind paywall), “Judge Lord based the ruling on a Supreme Court decision from 2014 that said companies can’t claim software patents for abstract ideas without inventive concepts.”
Here are the earliest 10 reports about it [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] (found this morning, so there might be more by now as it’s Saturday at noon).
Chalk or write another victory up on the blackboard/whiteboard. The Alice precedence is working. No wonder patent lawyers are in panic.
“Aggressive patent lawyers/corporations and their lobbyists, people like David Kappos, now have a war on SCOTUS itself.”“Why the S.Ct [Supreme Court] Should Not Be Deciding Patent Cases” is how Patent Buddy described this new attack on Justice Stephen Breyer. It oughtn’t be so hard to figure out why patent lawyers are very upset that SCOTUS is doing the right thing (against their greed). SCOTUS basically limits patent scope with decisions such as Alice, derailing patent aggressor as in the above example (less than a day old).
SCOTUS is intervening in various other areas and yesterday we saw this new comment stating: “Is the opinion discussed that of the Supreme Court or rather, as it appears to be, that of the 2nd Circuit? If the Supreme Court issued an opinion as well as an order, I for one would be interested to see it.”
Aggressive patent lawyers/corporations and their lobbyists, people like David Kappos, now have a war on SCOTUS itself. They view it is a threat and they wish to battle it using Congress (snitching on the lawmaker to other lawmakers). They hope to somehow make Alice go away. According to this new report by Professors Colleen Chien (Santa Clara University Law School) and Arti Rai (Duke Law School), the “USPTO hosted a day-long conference around the one-year anniversary of its Enhanced Patent Quality Initiative,” wherein, after intensive lobbying by Kappos, the predecessor of Lee, we have this: “In line with the case study suggestions, the USPTO aims to address concerns about particular types of examiner rejections and consistency across technology groups within the patent corps. To that end, it will be conducting studies on the use of section 101 and 112(f) by examiners; on the correctness and clarity of motivation statements in obviousness rejections based on combining references; and enforcement of written description requirements in continuation applications.”
“Expect patent maximalists to try to turn the table and propose regressive steps.”Don’t touch section 101. They’re hoping to regress back to pre-Alice days. Another new report says: “The USPTO recently requested proposals for case studies that the Office might do in order to improve patent prosecution. There were over 100 proposals submitted from associations, companies, law firms, and individuals. There are definitely some proposals that the USPTO should use. [...] All of these are great proposals, and each of them has the potential to either identify weak spots at the USPTO or confirm that examiners are following Office guidelines. Let’s hope the Office is giving these proposals serious consideration.”
Expect patent maximalists to try to turn the table and propose regressive steps. Boris Zelkind, “a partner focusing on litigation and intellectual property licensing in the San Diego office of Knobbe Martens,” has just said: “Additionally, as patents continue to take a beating in the courts and in the Patent Office’s post-grant reviews, companies need to consider whether their innovations are suited for trade secret protection. This is particularly true in the software world, where the US Supreme Court’s decision in Alice Corp. v. CLS Bank Int’l, created significant challenges to obtaining patent protection for software innovations and enforcing software patents. Thus, innovators in the software industry may need to be increasingly aware of trade secret laws and may be required to rely on such laws in order to protect their innovations.”
“Software patents may be down for the count in the United States, but don’t count on powerful lobbies not to pull them back up because they usually get what they want (at the end, sooner of later).”This is more of the same kind of maximalism. Patent lawyers, seeing that Alice has made software patents incredibly hard to attain and then assert/enforce, are openly promoting laws that would criminalise a lot of whistleblowers — the types of people who habitually offer us input about the EPO (nevertheless, trade secrets law is beyond the scope of our coverage). What’s noteworthy here is that there’s clearly a strong response to Alice and we ought to take note of who’s behind it. Software developers are happy about Alice, whereas patent lawyers and companies like IBM and Microsoft (huge patent aggressors) want the decision burned inside the ashtray.
Software patents may be down for the count in the United States, but don’t count on powerful lobbies not to pull them back up because they usually get what they want (at the end, sooner of later). According to Patent Docs, PTAB (increasingly and commonly an Alice enforcer) has just been invoked again (against yet another silly software patent*, as is common in the US) and it eventually denied a CBM review.
Techrights remains dedicated to exposing all the string-pulling behind the scenes as it’s abundantly clear that there’s a growing (and already very strong) movement to revive software patenting in the US. “The price of freedom is eternal vigilance,” Thomas Jefferson famously said. █
_____
* This patent being on software is evident and self-explanatory. To quote: “The ’805 patent is directed to a system and method for soliciting “page-specific” feedback from website users. User feedback is solicited on a page-specific basis by incorporating a “user-selectable element,” or “viewable icon,” into each web page of the website.”
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
Posted in Europe, Patents at 5:36 am by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
It is no secret that Battistelli resents the boards which he's increasingly afraid of

Summary: A critical evaluation of what goes on at the European Patent Office (EPO), which is quickly descending down (and overall degrading) to the level of Chinese systems, along with the corruption, the abuses, and the low quality of patents
THE EPO (speaking collectively of the management, not examiners) is a liar and a propagandist. It uses ‘creative’ statistics to make it seem as though things are all rosy [1, 2, 3] and Web sites which prefer to believe anything that EPO marketers claim still repeat the talking points, albeit there’s one element to it that can be counted more objectively, e.g.:
The number of inter partes oppositions decided increased by 17.6% to 3,713. In 31% of the decisions in opposition, the patent was maintained as granted. The percentage of patents revoked in opposition was also 31%. In the remaining 38% of the cases, the patent was maintained in amended form. The proportion of patents opposed was 4.4%.
The performance of the Boards of Appeal shows a steady state as regards the number of technical appeal cases decided. Some 2,387 technical appeals were received, of which 1,523 were opposition appeals and the remaining 864 were examination appeals.
What this generally tells us, in simpler terms, is that more than a thousand EPO patents were ruled invalid by the Boards of Appeal upon closer scrutiny. That’s a lot and some of these applications (not granted) which the board looks at are software patents in disguise (the G3/08 referral dealt with software patents more than half a decade ago). There can be billions of dollars at stake (bogus patents) and those who typically benefit from it exploit pressure and urgency against examiners. The EPO needs more of these boards and less of those maximalists who flaunt bogus figures, wrongly insinuating that more patents is more “production” (as if the goal is to just grant more and more patents irrespective of their merit).
This very recent analysis from a patent lawyers’ firm looked at IP5 Offices (the big patent offices) and stated: “The biggest difference in claims format between the IP5 offices is in the requirement for “one-part” versus “two-part” claims. The State Intellectual Property Office of the People’s Republic of China (SIPO) is the only office that mandates “two-part” claims, while the European Patent Office (EPO) prefers a “two-part” claim form. A claim is considered to be in “two-part” form if it lists some elements, then contains the phrase “characterized in that” or “characterized by,” and then lists one or more further elements. The latter elements (or the “characterizing portion”) are considered to be the novel or inventive features of the claimed invention, while the former elements are deemed to be found in the prior art. A “one-part” claim, on the other hand, does not identify any features as belonging to the state of the art. “Two-part” claims are not required or encouraged by the other three IP5 offices. The EPO also encourages reference signs placed within parentheses in the claims. The reference signs relate to technical features identified in the drawings of the patent application. Under European Patent Convention (EPC) Rule 29(7), the reference signs are only used for increasing the intelligibility of the claims and are not construed as limiting the claims.”
What we find amusing here is the similarity between the EPO and SIPO, which Battistelli evidently loves and emulates so much (including, apparently, human rights aspects of China). Just watch all those recent announcements and raves from Battistelli about SIPO (not the Croatian one from which Battistelli got his aggressive attack dog, Željko Topić). SIPO’s patent quality (and language barriers) is probably a lot worse than even the USPTO, where patent quality became a farce quite some time ago.
Battistelli is gradually killing the EPO by harming its reputation and lowering the quality of patents (which used to justify the very high prices of patents and renewals). Battistelli, an ENA graduate, is seemingly convinced that a race to the bottom is what will help the Office. How wrong is he. Battistelli, moreover, keeps lobbying for the UPC (even earlier this month), which would possibly make all or some of the boards redundant. It guarantees a decline in patent quality.
UPC boosters like MIP continue to pretend that the UPC is almost here (forget it, this might die pretty soon, just like previous incarnations) and a UPC monetisation firm now says that Lithuania is prepared to shoot itself in the foot with this UPC ploy. Have EU corporatists threatened nations with sanctions again (unless they adopt the UPC)? To quote the UPC monetisation firm:
The Lithuanian government has submitted draft legislation to the Seimas (the unicameral parliament) to enable Lithuania to ratify the UPC Agreement and to form, with Sweden, Estonia and Latvia, a regional division of the UPC. The draft legislation, submitted on 9 March 2016, includes: Bill to ratify the UPC Agreement, Bill to ratify the Agreement on the establishment of a Nordic-Baltic regional division of the UPC, and Bill to amend the Patent Law. The bills currently show a date of entry into force of 1 July 2017.
What Europe needs more of is independent boards. Those are the boards which, just like US patent courts, are able to objectively assess patents without the incentive to grant (unlike patent offices). The UPC goes against all that by potentially abolishing the boards and increasing costs (litigation rather than appeal at a board level with European-wide implications for ‘damage’ calculations and injunctions).
Battistelli is still out of his mind and he needs to be stopped. █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
Posted in America, Patents at 4:38 am by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
Another good reason to shut down CAFC once and for all
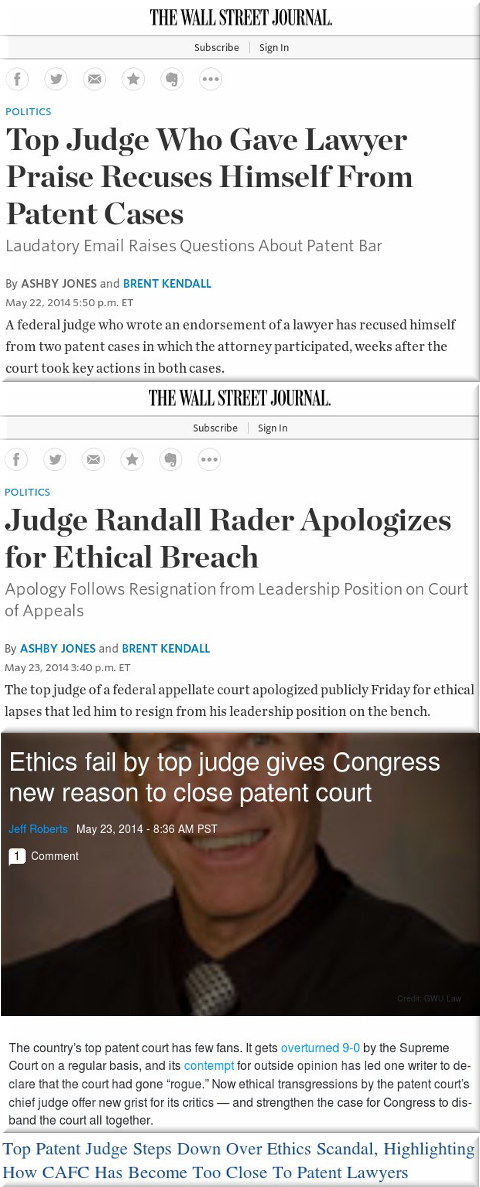
Summary: The notorious CAFC, which manifested software patents in the United States, has just given a gift to patent trolls that typically use software patents for extortion down in Texas
EARLIER this month and also last month we wrote about an effort to restrict patent trolls from taking their cases (or dragging defendants/victims) to ‘friendly’ courts, notably courts in the Eastern District of Texas where the majority of patent cases are now being filed. Well, sadly enough, the Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit (CAFC) has just sided with the trolls (inaction is taking a side in this case), just as it sided with software patents proponents several decades ago, opening the floodgates to almost a million more (patent trolls typically uses these).
“This will hopefully be escalated to the Supreme Court…”Professor Mark Lemley wrote that the “Federal Circuit won’t restrict forum shopping in patent cases. Next stops — the Supreme Court and Congress. http://src.bna.com/exf” (EFF is named in the cited PDF). Here is the statement issued by the EFF only hours ago:
In a disappointing but unsurprising ruling, the Federal Circuit confirmed today that patent owners essentially have free rein to file suit in any tiny corner of the country, regardless of its minimal connection to the patent owner, the alleged infringer, or the technology involved.
The case is In re TC Heartland. The alleged infringer, TC Heartland, was sued by Kraft in Delaware. TC Heartland asked the Federal Circuit, through a petition for writ of mandamus, to find that the case couldn’t be heard there, according to laws regarding “venue.”
Lemley cited the decision early on (the first we found on the topic), but Professor Dennis Crouch also adds some personal comments, stating: “In its petition for writ of mandamus, TC Heartland raised a set of interesting venue and personal jurisdiction claims – basically arguing that both the statute and Supreme Court precedent strongly limit where patent claims can be brought.”
This will hopefully be escalated to the Supreme Court, which unlike the CAFC isn’t quite so biased and even corrupt (we covered this many times before). █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
Posted in Intellectual Monopoly, Patents at 4:19 am by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
 Summary: Professor Mark Lemley’s Lex Machina highlights litigation trends by collecting and analysing data related to patents and pertaining to intellectual monopolies in general; now it shows litigation droughts
Summary: Professor Mark Lemley’s Lex Machina highlights litigation trends by collecting and analysing data related to patents and pertaining to intellectual monopolies in general; now it shows litigation droughts
“Lex Machina’s Hatch-Waxman/ANDA [Abbreviated New Drug Application] Report reveals a spike in case filing,” MIP wrote the other day, “as well as the biggest participants and law firms in ANDA patent litigation” (with low quality of patents, more lawsuits are assured).
We find it interesting that MIP chose to focus only on ANDA (one single aspect among many) because the figures from Lex Machina don’t show a spike in litigation overall. Selection bias? Cherry-picking perhaps, as any lawyer's means/method for constructing misleading (but nonetheless not false) statements? As a patent maximalism site has just put it, “IP litigation report shows downward trends in patent” and to quote the author (not the overzealous supporter of software patents): “Intellectual property litigation analytics firm Lex Machina has recently released a report identifying trends in IP litigation which have played out over the course of the first quarter of 2016. The first quarter saw some interesting developments in regards to decreases in certain types of litigation throughout the IP world. In fact, it could be argued that the number of IP cases filed were trending downward across the board during 2016’s first quarter.
“Even if the patent office continues to ignore the reality post Alice, courts certainly do not.”“Regular patent litigation reports released by Lex Machina in recent months have given us some insight into patterns forming over the past few years. An early January post on litigation trends during 2015 reflected steep increases in patent litigation and the dominance of certain U.S. district courts in receiving those cases. A larger 2015 patent litigation report published by Lex Machina in March showed us the top litigants and asserted patents during the course of that year.”
As we are going to show in later posts, software patents continue to die in the US, no matter what the lobbyists are trying to achieve. Even if the patent office continues to ignore the reality post Alice, courts certainly do not. The patent office is in general incentivised to grant more and more patents, whereas courts produce judgments based on law. █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
Posted in Asia, Patents at 3:46 am by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
Low-quality software patents (on abstract ideas) are keeping India controlled by foreign multinationals

Bangalore, India
Summary: The growing software giant which is India continues to face cruel and aggressive lobbying from the West, enabling the West to control India by patents that should not exist in the first place
INDIA is currently under a lot of pressure from US lobbyists because it repeatedly rejected software patents. In recent weeks alone we saw the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) putting India under pressure and days ago it was USTR. Colonialism never truly ended and the empire of corporations vainly assumes that it can impose on India whatever law it desires.
“Don’t listen to the IT giants” is the headline of this new article from the Indian Express, which even quotes Bill Gates to highlight his hypocrisy (Microsoft is among the forces now lobbying India for software patents). To quote the start of this good article:
The Indian government has rightly rested its Digital India initiative on a series of measures to liberalise the economy. One of those measures of free-market wisdom, however, the usual government-cheering section suddenly seems to be irrationally against. The PMO will be receiving from the Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion (DIPP) on April 30 a report on the Patent Office’s Computer-Related Inventions Guidelines (CRI), in which parties who usually applaud free-market measures are horrified to discover that Section 3(k) of the Patent Act really does prohibit government-awarded monopolies in software, and that the controller of patents is implementing the statutory command.
Software patenting is not a requirement of TRIPs, or of any current international trade law. The controller’s new CRI guidelines actually implement a test for software per se — unpatentable owing to Section 3(k) — which is close to the “machine or transformation” test all-but-imposed by the US Supreme Court in a series of cases over the last five years, in all of which we were amici curiae, urging the court in its current direction.
Software patenting is not in the Indian national economic interest. “Software,” as Bill Gates used to say, “is an IQ business”. When non-Indian firms can get software patents in India, the effect is to hobble the Indian IQ advantage, by making what many talented Indian programmers could otherwise use to make new innovations in software the property of the non-Indian patenting company. As our organisation, SFLC.in, has shown in its research report on the subject, more than 90 per cent of software patents awarded in India, before the rectification imposed by the new guidelines, were issued to foreign corporates.
Incidentally, looking elsewhere in yesterday’s news, Ericsson comes under fire in India because of its use of patent trolls (also in the EU) to extract money out of competitors, using — in part — software patents. As one article put it yesterday: “In March 2013, the Swedish multinational Ericsson sued Micromax for patent infringement, setting in motion a series of events, with the potential to disturb India’s mobile phone dream. Then last month the Delhi High Court recognised the authority of the regulator – the Competition Commission of India (CCI) – to probe Ericsson for its allegedly anti-competitive conduct.”
Indians should get more active (in the activism sense) and work to abolish software patents in India once and for all, identifying all those occupying forces that keep trying to revive the effort for software patents in India (including new loopholes for these). Not only does India have nothing to gain from software patents; it has a lot to lose from them. █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend




 Summary: Professor Mark Lemley’s
Summary: Professor Mark Lemley’s 
















 Content is available under CC-BY-SA
Content is available under CC-BY-SA