10.10.16
Posted in Europe, Patents at 8:19 pm by Dr. Roy Schestowitz

Source (original): Rospatent
Summary: A concise new letter explains the situation at the EPO and what Battistelli is planning to do next, especially if the Administrative Council gives him a carte blanche, as usual
THE heads of the delegation of the Administrative Council of the EPO are about to meet and the following letter is being sent to them from staff that, as a matter of survival, must remain anonymous. Below is the content of the letter:
Open letter – by email to the Heads of Delegation
11 October 2016
Copies to:
Competent Ministries of the Member States
The social situation at the EPO and the Administrative Council’s responsibility
Dear heads and members of the delegations to the Administrative Council of the European Patent Organisation, dear Chairman, dear Mr Grandjean,
We would like to share our concerns about the current social climate at the EPO and urge you to take appropriate action.
‘Social Conference’ – how to avoid social dialogue
You will probably agree that in any organisation the first step towards genuine dialogue is to work towards a shared understanding of the problems at hand and of the long term goals, in other words, to share an agreed agenda. This seems a reasonably evident requirement for the future success of the EPO. Sadly, the Office missed a chance to take a first step towards this, when it alone set the agenda of the ‘Social Conference’ scheduled for 11 October. Consultants will present a ‘social study’1 while the President refuses to discuss the results of a staff survey2 commissioned by the EPO’s largest staff union. It is difficult to imagine how even the seeds of social dialogue can exist while the Office continues with its unilateral approach to the most multilateral of issues. The President’s threats to and persecution of elected representatives3 of his social partner only serve to shift the situation from bad to worse. Through his actions he makes social dialogue impossible. For staff across the Office, the ‘Social Conference’ can only be seen as just another useless attempt to mould a distorted perception of the reality at the EPO. And to avoid true social dialogue.
The social situation at the EPO – a matter of perception?
You may already have seen a letter of the President of the Dutch Institute of Patent Attorneys, ‘Nederlandse Orde van Octrooigemachtigden’ (Orde)4, dated 12 February 2016 and addressed to the Council, which recently became public5. The Orde perceives the social climate in the Office as follows:
‘… We note that, when we seek information from EPO employees, they are reluctant to communicate in fear of retribution by internal investigative units. It seems that the people at the EPO are afraid of their own management. The Orde rejects this situation vehemently. We cannot understand that the President of an organization that envisages to “set worldwide standards in quality and efficiency“ is not capable or not willing to apply the same standards to its people management. We refer also to the ruling of the Dutch Appeal Court that the EPO appears to be violating basic human rights.
A disgrace, irrespective whether the EPO benefits from its immunity as an international organisation or not. A reputable international organization such as EPO should not have it’s employment conditions and employee rights held up against such a basic thing as human rights.’
Consequences of the current social climate for the future of the European patent
It is illusory to think that a human resources policy without any negotiation, founded on intimidation and the non-respect of fundamental rights can bind highly skilled staff to the Organisation. The Orde is right to use the word “disgrace” to describe any violation of human rights that takes place at the EPO. No amount of immunity can diminish that disgrace. Disengaged and demotivated employees will clearly not be able to examine patent applications with the critical focused mind needed for delivering a legally valid monopoly right. We cannot imagine that the delegations to the Administrative Council still believe that it will be possible to maintain a successful European patent and foster economic growth without the active support of staff. We certainly don’t.
An estimated6 2016/2014 increase in production (+ 23%) and productivity (+11%) is not a sign of successful reforms but rather proves that the examiners have lost any ambition to withstand unrealistic and arbitrary production targets imposed on them by the Administration. The current management style has destroyed staff’s professional attitude and pride to work for an organisation whose aim is, or at least was, to support economic growth by delivering high quality patents. It is our view that the European Patent Organisation finds itself in the deepest crisis7 of its history.
The currently planned reforms, if adopted, would aggravate the crisis
If proposal CA/53/16 Rev. 1 (reviewed Disciplinary Guidelines) gets approval, Mr Battistelli will be in a position to dismiss staff members for ‘professional incompetence’ without any meaningful advisory review instance. He will be able to expose EPO employees to unemployment without the safety net of a social security system. For fear of dismissal, staff will no doubt do their best to deliver another productivity increase. The quality of search reports and the legal validity of European patents will drop further.
By adopting the reviewed Investigation Guidelines (CA/52/16 Rev. 1) the Council would authorise the Administration, i.e. Mr Battistelli, Mr Topić and Ms Bergot, to proceed with investigative and disciplinary proceedings in a way that is in contradiction to the principles of due legal process. Before adopting any revised proposal, we ask the delegations to consider the recent proposal for WIPO’s new Investigation Guidelines8. WIPO has immense problems in its staff relations. But in this case, they seem to have put forward a balanced proposal, at least on first inspection. It takes account of lessons learned9, provides an independent investigative unit, and guarantees due process and whistle-blower protection, including the case of investigations against senior officials10.
Please do not support the current proposals CA/52/16 Rev. 1 and CA/53/16 Rev. 1. There can be no doubt that they give new tools of abuse to those at high level who wish to use them, and increase the risk of victimisation, harassment and miscarriages of justice in a system that is already under fire for not fulfilling the requirements of legal process.
Staff protest against the treatment of their elected representatives by the President and the passive attitude of the Board 28 vis-à-vis this issue in its recent meeting3. We kindly ask all delegations to remember the AC’s resolution 11 of this March and to take the steps that must follow it:
“to ensure that disciplinary sanctions and proceedings are not only fair but also seen to be so, and to consider the possibility of involvement of an external reviewer or of arbitration or mediation
pending the outcome of this process and before further decisions in disciplinary cases are taken, to inform the AC in appropriate detail and make proposals that enhance confidence in fair and reasonable proceedings and sanctions;”
We further plead that matters of such grave concern no longer be discussed in closed session. Arguments put forward need to be visible to the affected parties, being staff and applicant community.
With our best regards,
The EPO-FLIER team
a group of concerned staff of the EPO who wish to remain anonymous
due to the prevailing harsh social climate and absence of rule of law at the European Patent Office
_________
1 European Patent Office – Social Study 2016, by PwC
2 https://www.suepo.org/results_of_the_2016_european_patent_office_staff_survey/d-43311
3 B28/10/16 (21.09.2016): “the Board noted information provided by the President about three current investigations/disciplinary proceedings involving SUEPO members in The Hague”
4The Dutch Institute of Patent Attorneys is the professional organisation of Dutch patent attorneys; its about 500 members are active in private practice and in industry, most of them are also European Patent Attorneys
5 http://techrights.org/2016/09/29/netherlands-institute-of-patent-attorneys-on-battistelli/
6 http://techrights.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/sc16170cp.pdf
7 B28/2/16 (02.02.2016): “The Board qualified the situation as a crisis – a view challenged by the President.”
8 http://www.wipo.int/edocs/mdocs/govbody/en/wo_ga_48/wo_ga_48_16.pdf
9 http://www.ip-watch.org/2016/09/30/gurry-speaks-on-allegations-for-first-time-as-wipo-members-discussion-actions
10 http://www.ip-watch.org/2016/10/10/members-debate-changes-to-oversight-at-wipo/
11 http://www.epo.org/about-us/organisation/communiques.html#a23
I have taken two day off work this week. We can hopefully provide coverage of what happens as the media sure isn’t doing its job. We more or less know why. █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
Posted in America, Patents at 7:03 am by Dr. Roy Schestowitz

Summary: The Federal Trade Commission’s report about patent assertion entities (euphemism for a particular type of patent trolls) is bad news for patent trolls and potentially the catalyst of upcoming patent reform
Having published "Towards the End of Patent Trolls-Friendly Courts in the United States" and "Towards the End of Software Patents in the United States", we finally turn our attention to the FTC’s new study, which comes at a good time because of those former two installments (about courts in Texas and software patents, not to mention Apple’s stupid software patents that it uses to demand hundreds of millions of dollars — a subject of plenty of media coverage at the end of last week).
The USPTO is partly to blame here, for reasons that the Government Accountability Office (GAO) explained a few months back. Patent trolls use software patents quite a lot; without these patents, patent trolls would almost cease to exist. We wrote about evidence of that in the distant past.
“Patent trolls use software patents quite a lot; without these patents, patent trolls would almost cease to exist.”So, what has the FTC just shown us? In the words of CCIA, which took money from Microsoft after it had gone after it: “Ed Black said trolls are exploiting #patent system for a quick buck so we appreciate the #FTC ‘s patent troll study pic.twitter.com/AKdQFRBo19″ (there’s a photo in there).
“The FTC study on PAEs is finally out. A long report with a lot of useful data. It will take a while to parse it all,” wrote Professor Risch, who at times sounded like he defended software patents (several times in the past).
“FTC patent assertion entity study recommends fixing discovery asymmetries,” wrote another person, “mandating more disclosure by PAEs; streamlining litigation…”
“Long awaited @FTC study on patent assertion calls for strong patent reform,” wrote one character upon a quick glance.
More press coverage regarding the FTC’s study (that would likely transform the whole of the US patent system through upcoming reform) was soon generated, starting with blogs like this one:
FTC Releases Big Report On Patent Trolls, Says The Patent System Needs To Change
[...]
For quite some time now the FTC has been making lots of noises about the problems of the patent system and patent trolls in particular. While the US Patent Office itself has done little to address the problem, the FTC has recognized the harm patent trolling is doing to innovation and consumers. More than five years ago, the FTC released a big report on patent trolling and the problems it causes — suggesting that the Patent Office should start getting rid of vague patents with “indefinite” claims. That has happened a little bit, but much more because of the Supreme Court forcing the issue, rather than the USPTO listening to the FTC.
However, since then, it’s appeared that the FTC has only grown more concerned. Basically every year we report that the FTC is investigating patent trolls in some form or another. In 2012 (a year after that first report), the FTC began exploring patent trolling more thoroughly. In 2013, it announced an official investigation that would make use of subpoenas to find out how patent trolls were actually operating. Later that year it was revealed that it would subpoena 25 patent trolling operations. Since then, though, it’s been mostly crickets. There was one famous troll, MPHJ, who sued the FTC in a case that was dismissed.
And now, finally, after all these years, the FTC has released its big report. It appears that 22 patent trolling operations responded to the subpoenas, though many had “affiliates and other related entities” allowing the FTC to study many more patent trolling operations overall. The study lumps patent trolls (they prefer the euphemistic “Patent Assertion Entities” or PAEs) into two categories: litigation trolls and portfolio trolls. In short, litigation trolls are the smaller guys with just a small number of patents, who would threaten and sue companies (and quickly reach settlements) over those few patents. It’s more of a “mom & pop” shakedown kind of business. Portfolio trolls are the bigger, well funded operations, that have a massive portfolio of patents and play a more comprehensive shakedown game, going to lots of big companies and basically saying “you infringe on some of our patents, so give us a bunch of money to not figure out which ones.” Think: Intellectual Ventures or Acacia.
The differences here matter, because the businesses are quite different. Lots of the actual lawsuits come from the litigation trolls as a sort of negotiation tactic. The portfolio trolls don’t actually have to go to court that often — they have “sales people” who are a bit more effective. But the amount of dead-weight loss to the economy from the portfolio trolls is much larger. When big companies agree to a portfolio troll shakedown it’s often for a tremendous amount of money. The FTC study found 80% of the revenue went to portfolios, and only 20% to litigation trolls — even though litigation trolls filed 96% of the lawsuits and 91% of the reported licenses.
One interesting — and potentially surprising — finding of the study was that the FTC did not see evidence of much pure demand letter shakedown. That is, it’s been said that many of the smaller trolls just send letters, but never expect to go to court, since many may just settle based on the demand letter. But the FTC didn’t find much evidence to support that — saying that most of the revenue for litigation trolls came from actually going to court (and then rapidly settling). In short, it appears that the leverage of a federal lawsuit (in eastern Texas, probably) is much stronger than just a threat of a lawsuit. But a key takeaway from this is that attempts to reform demand letters (which has been regularly proposed — such as requiring them to outline what the infringement is) won’t actually help much.
Almost everyone (except trolls) would agree that the patent system in the US needs fixing. See this new article (“Patent reforms must also include our trade courts”) and a National Retail Federation press release (“FTC Study Should Provide Momentum to Pass Patent Reform Legislation”), not to mention a growing bulk of media coverage, such as [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]. More media coverage of this kind will continue this week, with patent trolls getting negative publicity after people actually read those hundreds of pages and summarise what’s in them. See “Public Knowledge Applauds FTC’s Call for Strong Patent Litigation Reform” and the excellent early coverage from Jeff Roberts, who said that the “FTC has harsh words for patent trolls – what tech folks have been saying for years http://fortune.com/2016/10/06/ftc-patent-report/ …”
“IAM is nowadays doing to journalism what the US presidential candidates already do to journalism. So-called ‘news’ sites pick a side and hardly pretend to be unbiased observers.”“Both Mayer and the FTC,” I told him, “say what we’ve been saying for years, e.g. code is like prose and protected by copyright” (Roberts liked that). The patent mess in the United States is being tackled little by little; almost exactly 5 years ago Obama signed one patent reform bill and soon there will be another.
IAM’s Mr. Lloyd, quite proudly a proponent of software patents and all sorts of other nuisance, decided to go against the flow because IAM is not really a news site. The voice of the patent trolls, IAM ‘magazine’ (partly funded by trolls), attacks the FTC for saying the truth about them. It’s quite laughable that all they could say (in the headline) about the news is that it “is probably already out of date” (got to be seen to be believed).
IAM is nowadays doing to journalism what the US presidential candidates already do to journalism. So-called ‘news’ sites pick a side and hardly pretend to be unbiased observers. Here is Watchtroll; watch how his site spins the study against troll as pro-trolls — because hey! — it’s not journalism anyway, just lobbying. Talk about lying to or misleading readers.
What did MIP do? Well, it resorted to shooting the messenger or its intelligence, as usual. To quote a portion from this article:
The Federal Trade Commission’s long-awaited patent assertion entity report differentiates between portfolio PAEs and litigation PAEs. The Innovation Alliance has called it an “unscientific case study”
The Innovation Alliance is a think tank, much like the Scientific Alliance and Copyright Alliance. It calls the FTC’s study an “unscientific case study” because its paymasters are unhappy with the findings.
Here is the original page about this study:
A new Federal Trade Commission report spotlights the business practices of patent assertion entities (PAEs), firms that acquire patents from third parties and then try to make money by licensing or suing accused infringers. The report includes several recommendations for patent litigation reforms.
“This report is a big step forward in enhancing our understanding of PAEs and provides an empirical foundation for ongoing policy discussions,” said FTC Chairwoman Edith Ramirez. “The recommendations we are proposing are designed to balance the needs of patent holders with the goal of reducing nuisance litigation.”
Patently-O did a fairly decent job covering it (it’s the first such coverage we found):
The report offers important insight into PAE business models – primarily identifying two categories: Litigation PAEs and Portfolio PAEs. The FTC found that Litigation PAE licensies are “typically … less than the lower bounds of early stage litigation costs” and thus seen by the FTC as consistent with “nuisance litigation.” The report suggests a variety of litigation reforms to help alleviate potential abusive litigation tactics by patent owners.
The 269 page report will be a catalyst for patent reform measures and thus should be considered carefully.
I have not personally read this report, but rest assured the patent microcosm and its front groups will attack both the messenger and the message by all means possible. They’ll do anything to derail patent reform that puts an end to (or significantly curbs) patent trolls. █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
Posted in America, Patents at 6:10 am by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
The patent microcosm is hopping mad and in denial over it
Summary: A closer look at the latest historic decision on software patents and other news serving to cement the end of software patents in the United States (provided the cases are appealed upwards)
THE USPTO is gradually departing from software patents, whereas the EPO goes the other way. Does that mean that elimination of software patents in the US would not be sufficient in extinguishing the scourge of software patents worldwide? Maybe. But at least progress is being made in the birthplace of software patents. Today’s article binds together many bits of coverage, focusing in particular on the Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit (CAFC).
There are many ways by which to weaken or thwart patent litigation. One such way, as noted the other day, is blurred allegations. As Patently-O put it, “Lyda appears as a narrow decision against an individual-inventor plaintiff, the decision is important because it establishes that a patent infringement complaint must provide factual allegations at the claim-element-by-claim-element level in order to avoid a dismissal on the pleadings.”
Distracting From Haldane Robert Mayer
What is more interesting, however, is dismissal based on the two-step analysis — something which has happened a lot since Alice and we wrote about thrice since a decision was handed down by Judge Haldane Robert Mayer of CAFC. We are hardly shocked to discover the patent microcosm either refusing to write about it or simply attacking the judge, as we shall show later. Robert R. Sachs of Bilski Blog seems to be among those who simply said nothing about it. Instead, quite a while after the decision from Judge Mayer, he instead wrote about a bundle of cases in favour of software patents. To quote: “For patent prosecutors, MAZ, along with DDR, Enfish and McRo, suggests the value of discussing in the patent application specific problems in the prior art and linking aspects of the claimed invention to their solutions. The general trend over the past several years has been to say less in the background and summary of invention. That is still good advice, and these cases do not contradict that view, as the underlying patents provided very short and concise statements of the prior art problem, not lengthy expositions. Prosecutors that draft only a trivial background and little or no summary of the invention may end up removing an important basis for establishing eligibility and defeating an early dispositive motion. If the motivation for this approach is the risk that the background and summary will narrow the scope of the claims, I would say better a slightly narrowed patent than none at all.”
David Kappos Still Lobbying
What is worth noting here is that patent attorneys and lawyers are still looking for ways to work around the law and patent software in spite of the rules. Here we have some patent law firms scrambling to find tricks for patenting and asserting software patents; see “4 Tips For Overcoming ‘Abstract Idea’ Rejection” or (less relevant) “Anything You Say Can and Will be Used Against You in a Court of Law”. It’s part of a pattern. They write many articles about it and even set up events on the subject. One new event from IAM, advertised just before the weekend, targets patent maximalists and features a corrupt judge, Rader, and an official-turned-lobbyist, David Kappos. IAM ‘magazine’, one might note, evidently doesn’t keep good track of judge names; they spell a key name with a typo, “Radar”, not Rader. To quote the event’s overview: “Are patents in the United States dead? Should US companies continue to file US patents? What are the right innovation policies for the United States? What is the right thing for small companies to do in patenting their innovation? How will investors look at patenting in the future? What is happening elsewhere in the world? Come and join this critical discussion with Radar, Kappos, Schramm, Cabeca and others.”
Kappos is, in our view, the most corrupt public official in this domain, turning from a public official at the Patent Office into a corporate lobbyist for Microsoft, IBM, etc. Are they not at all regulating what people do after their service at the PTO? Is there no cool-off period? Nothing? Watch this news article entitled “Kappos: McRO is CAFC’s “most important 101 case since Alice””. To quote:
“McRO gets to the core issues and for that reason I thought it’s clearly the most important 101 case the Federal Circuit has put out since Alice” – David Kappos”I didn’t see a tremendous amount of the principle or the reasoning in those previous cases,” David Kappos, partner at Cravath Swaine & Moore
This doesn’t disclose that he’s also a lobbyist. Cravath Swaine & Moore is not his sole source of income.
CAFC said copyright should be enough for software, but this continues to be ignored by Kappos and the rest of the software patents boosters, who develop no software at all. They just lean on cases like McRO even a month later.
PTAB is Still Invalidating a Lot of Software Patents
According to this page from the USPTO and an article about it, PTAB fees might soon go up. PTAB has played an important role in improving the USPTO (well, at least quality is improving), but a rise in fees would discourage appeals; the same thing was attempted at the EPO. It has meanwhile turned out that the (in)famous appeal from Kyle Bass (the patent microcosm calls “trolls” those invaliding patents, as in this case where they used to dub the appellant “reverse troll”) was not successful. The appeal was not about software patents however.
Michael Loney of MIP shows that PTAB continues to invalidate software patents at a steady pace; there are no signs of stopping or slowing down. There are charts in the page that says:
Managing IP reveals Patent Trial and Appeal Board filing figures for September and the third quarter, as well as ranking the top petitioners and patent owners for the first nine months of 2016. More PGRs than CBMs were filed for the first time ever in September
The third quarter has ended with 454 Patent Trial and Appeal Board (PTAB) petitions filed, down only slightly on the 459 petitions filed in the second quarter.
Expect this to carry on for quite some time because SCOTUS certainly isn’t overturning Mayo and Alice. As one article put it the other day (in the headline), “The Supreme Court Refuses To Consider Patents Invalidated Under The Mayo/Alice Framework”. It’s just done with that and given how long it has been since the Bilski case, it might take another half a decade before anything can really change (or reconsidered).
Copyrights — Not Patents — for Software
The main theme in this past week’s news about patent was something along the lines of Haldane Robert Mayer’s ruling, which we covered here several times before. He asserted that copyrights should be sufficient in the domain of software and a new article entitled “Copyright Tools for Protecting Software” got published. SCOTUS “limited the field of software patentability,” it says, hence software developers should focus on copyright, not patents. To quote from the article:
For businesses that run on software, protecting intellectual property is even more important than locking the office door at night. IP protection in the United States comes in many forms, including patents, copyrights, and trade secret laws. Patents have long been considered the gold standard in intellectual property, in large part because they protect inventive concepts and are not limited to specific expressions. However, software companies should think beyond patents in protecting their IP, especially since the Supreme Court in 2014′s Alice Corp. v. CLS Bank International, 134 S. Ct. 2347, limited the field of software patentability, and the Post Grant Review system installed by the America Invents Act (Pub. L. 112-29) invalidates more software patents by the day.
Regarding the ruling from Haldane Robert Mayer, it was everywhere in the news and people also brought that up in our IRC channels. Consider articles such as “A judge wants to make patent trolling a first amendment issue” (The Verge) and “WHAT DO SOFTWARE PATENTS AND ‘CHINATOWN DANCE ROCK’ HAVE IN COMMON? FREE SPEECH” (Bloomberg). Also see Mike Masnick’s take on it over at TechDirt. It’s titled “Prominent Pro-Patent Judge Issues Opinion Declaring All Software Patents Bad”. It actually upset Bastian Best, a patent attorney from Germany. “Most people declaring “all <insert subject> are bad” should not be taken too seriously,” he wrote about this article and I told him that it sounded like had made a joke, along the lines of a famous saying from Alexandre Dumas: “All generalizations are dangerous, even this one.” (there are variants of this quote from other people)
In relation to another one of Best’s tweets, Benjamin Henrion wrote, “we believe you. Patent law is a religion…”
Anyway, here is what TechDirt actually said in its article, having followed this subject very closely for many years:
Well here’s an unexpected surprise. A lawsuit brought by the world’s largest patent troll, Intellectual Ventures, and handled on appeal (as are all patent cases), by the notoriously awful Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit (CAFC) may have actually killed off software patents. Really. Notably, the Supreme Court deserves a big assist here, for a series of rulings on patent-eligible subject matter, culminating in the Alice ruling. At the time, we noted that you could read the ruling to kill off software patents, even as the Supreme Court insisted that it did not. In short, the Supreme Court said that any patent that “does no more than require a generic computer to perform generic computer functions” is not patent eligible. But then it insisted that there was plenty of software that this wouldn’t apply to. But it’s actually pretty difficult to think of any examples — which is why we were pretty sure at the time that Alice should represent the end for software patents, but bemoaned the Supreme Court not directly saying so, noting it would lead to lots of litigation. Still, the impact has been pretty widespread, with the Alice ruling being used both by the courts and the US Patent Office to reject lots and lots of software and business method patent claims.
But this latest ruling, from the very court that upended things nearly two decades ago in declaring software much more broadly patentable than anyone believed, may now be the nail in the coffin on software patents in the US. The headline, of course, is that the patents that Intellectual Ventures used against anti-virus firms Symantec and Trend Micro, were bunk, because they did not cover patent eligible subject matter. But the part that has everyone chattering is the concurring opinion by Judge Haldane Mayer, that says it’s time to face facts: Alice killed software patents. And Mayer is not some newcomer. He’s been at the Federal Circuit since the 1980s and was actually the chief judge in the late 90s/early 2000s when CAFC was at its worst in terms of expanding patent law. And it appears he’s been born again into the anti-software patent world. It’s… quite a conversion.
Yes, exactly, and this reversal is noteworthy, as we said here many times before. “The greatest expansion in what software is patentable,” the above continues, “occurred when Judge Mayer was chief judge of the USCAFC. Judge Mayer oversaw the creation of software patents. Now Judge Mayer has written an opinion which fully agrees with the points made by any of the anti-software patent people, including me.”
Hence the great significance of it. Not only is the pro-software patents court making a 180-degrees turn; it’s even that particular judge.
A short post by Thom Holwerda was succinctly (but right to the point) titled “US judge: end software patents, copyright is sufficient” and bloggers like Pogson cited the above, stating: “Over on Tech Dirt, there’s TFA about a ruling of a court that could pound in the last nail of the coffin of “software patents”, you know, patents on stuff that’s not patentable because it looks new and shiny just because it’s coded into a computer…”
Readers have told us that even Danish media covered it (we imagine a lot more all around the world); the translation of the headline is roughly “Have software patents died?”
Combining the FTC study (to be covered later and separately) with the CAFC ruling that names software patents as well as patent trolls (the plaintiff was the world’s biggest patent troll, Intellectual Ventures), we can imagine that there were many depressed patent lawyers this past weekend. Here is another news headline: “Circuit Court Judge Has Finally Had It With Software Patents” (from Mother Jones). To quote Kevin Drum:
The interesting thing here is that this was written by a longtime judge for the Federal Circuit Court: Haldane Mayer, a Reagan appointee who is now on senior status. Apparently, Mayer has had enough. In a recent case involving a patent troll, he didn’t feel like fiddling around on the edges of the Alice test handed down recently by the Supreme Court. He believes that Alice effectively does away with software patents entirely. Instead, software should be governed by copyright, as it was for decades before a series of vague rulings and the establishment of a new court accidentally created them in the 70s and 80s.
Mayer’s analysis is just a concurring opinion and has no legal force. Still, it’s encouraging that an experienced judge is saying stuff like this out loud. Maybe a few other will now follow suit. And maybe the Supreme Court will eventually agree. Maybe.
Getting Nasty and Attacking the Judge
The judge above is now being attacked pretty viciously by Watchtroll. We expected this. Joff Wild, the editor in chief of IAM ‘magazine’, made it very clear to me that he’s an adamant supporter of software patents and he had no coverage of this key case until about a week later. These guys were looking for spin, we presume… but they were not alone. The patent microcosm, by attacking a judge who has demolished some software patents, is basically defending a very nasty patent troll here. Is that a clever thing to do?
“Just When You Thought the Federal Circuit Was Softening Restrictions on Software Patents, the Tide Turns Again,” wrote another outspoken patent maximalism site (which habitually mocks judges). To quote:
Intellectual Ventures I LLC (“IV”) sued Symantec Corp. and Trend Micro (defendants) for infringement of various claims of three U.S. Patents (Nos. 6,460,050; 6,073,142; and 5,987,610). The District Court held the asserted claims of the ’050 patent and the ’142 patent to be ineligible under § 101, and the asserted claim of the ’610 patent to be eligible. The Federal Circuit affirmed as to the ineligibility of the asserted claims of the ’050 patent and ’142 patent, but reversed as to the asserted claim of the ’610 patent, resulting in finding all asserted claims ineligible under § 101.
Some reasoning applied during the two-step analysis, and in particular when finding that the patents are “directed to abstract ideas,” is not clearly provided by the Federal Circuit. The analysis for each of the three patents is summarized below. This decision just muddies the waters following other recent patent-owner friendly decisions in which the Federal Circuit seemed to be creating more ways for software patents to survive.
The decision further includes quite an interesting concurrence in which First Amendment rights were discussed as being implicated with Software patents?? Further comments will be provided on the concurrence alone.
This article was relatively polite (for this site), but as expected, Watchtroll went truly nasty. “It did not took [sic] long for the software patent boosters to react to Free Speech clash,” Henrion noted (also see “it did not took long to react to the free speech clash.”) and this nasty piece was the accompanying link. Watchtroll has even exceeded our own expectations and he was propped up by Patently-O and by IAM ‘magazine’ (though we assume linking is not the same as endorsing). IAM said: “No holding back here from Gene (or the many other commenters) on the subject of Judge Mayer, Alice & software patents!” (linking to this tweet)
“Well done,” I told the patent microcosm, “for making yourselves look like an enemy of society and also the court system…”
Henrion added that it happens “when someone is making your job irrelevant.”
“So whether computer programmers think software should be patented is completely irrelevant,” he remarked. Watchtroll (Gene Quinn) does not even know how computer programs work. I debated him over it in hundreds of tweets before he just ran away and blocked me (not that I said anything rude). “Let’s continue the swpat discussion here,” Henrion wrote, “it is fun to rehash the arguments with the other side” (even if it feeds the trolls, like Watchtroll).
If Watchtroll represents “the other side”, then Mayer et al would use Alice even more frequently and crush software patents for spite. Misleading headlines from the likes of Gene Quinn show us that the patent microcosm and software patents proponents aren’t just liars but also morally corrupt. The patent microcosm and those boosters not only attack the Supreme Court (Justices) but also lie about and smear judges. So who’s the rude side? By failing to distance itself from Gene Quinn and habitually contributing to Watchtroll’s site, the patent microcosm associates itself with nasty behaviour. The patent microcosm has gotten so bad and rude — because software patents are a dying breed — that they falsely make mental claims on judges (claiming them to be mentally deranged or ill), even impotence. Mocking sexual health (by connotation at least) of judges is about as low as one can stoop. The patent microcosm and these software patents boosters do themselves a huge disservice here. See our recent article "With Patent Law Firms Like These, No Wonder There's Distrust and Animosity".
Andre Rebentisch (FFII) wrote: “Apparently judge-bashing is considered appropriate in the US as @ipwatchdog shows. Just gets awkward when they target European ones.”
For those who are curious to know what Watchtroll wrote, here are some portions of it, calling for the judge to resign:
It has been obvious for some time now to any objective observer, but recent events make it such that it is time for someone to say it openly. Judge Haldane Robert Mayer, former Chief Judge of the United States Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit, should step down and move quietly into retirement.
For years Judge Mayer has had his own – shall we say “unique” – view of patent law. He has made a habit out of writing his own rather eccentric anti-patent views into dissents and concurring opinions and then later citing to himself in those dissents and concurring opinions as if they were somehow authoritative. If an attorney were to do something like that they would wind up being sanctioned, as ultimately happened when the Federal Circuit rebuked attorney James Hicks for mischaracterizing prior holdings and rulings in a brief submitted to the Court. But when a Federal Circuit Judge does such things we all just shake our head and sigh.
[...]
Simply stated, the industry and the public deserve better than Judge Mayer. His anti-patent views seem to have matured into an irrational hatred that so cloud his judgment that he twists, exaggerates and misrepresents in order to attempt to impose his radical views into the law. There is no place for a judge like that. It is time for him to leave the Court. If he chooses not to step down it would seem appropriate for the Court to do what they would with an attorney who grossly exaggerates and mischaracterizes cases and rulings to the point of misrepresentation.
IAM, by the way, was hardly much better. It is in denial of course, and with a biased, belated headline too (almost a week late): “No – the CAFC’s Justice Mayer has not just brought an end to software patents or anything close” (yes, the headline starts with the word “No”, just to remind us it’s not really a news site). To quote: “Software patents are not about to be suddenly ripped up thanks to Mayer’s comments – if it wanted to, the Supreme Court could easily have done that by now. What is more plausible is that in writing his concurrence, Mayer is really speaking to an audience of his fellow judges and, perhaps alarmed by recent decisions like McRO, he’s attempting to place a brake on the string of recent pro-software patent decisions.”
They are quoting Manny Schecter, chief software patents propagandist at IBM, as saying: “It is hard to understand why Judge Mayer would push the Federal Circuit “to acknowledge that Alice sounded the death knell for software patents” given that the Supreme Court in Alice did not refer specifically to software, appeared to be warding off this type of sweeping conclusion when it indicated that we must “tread carefully in construing this exclusionary principle lest it swallow all of patent law”, and (contrary to Judge Mayer) stated: “There is no dispute that a computer is a tangible system (in §101 terms, a “machine”), or that many computer-implemented claims are formally addressed to patent-eligible subject matter.” Furthermore, let’s not lose perspective. Judge Mayer is a single judge on the Federal Circuit, which we know to be deeply divided on this subject – recall the inability of the Federal Circuit to reach consensus in Alice when it reviewed the case en banc. My problem with Alice is not that it banned software patents (because it did not), but that its failure to provide clear guidance has resulted in a torrent of uncertainty.”
Law Firms Said Nothing or Resorted to Misdirection
Well, finally, almost a week and a half later, one law firm covered the case, under the headline “Judge Mayer Finds that Section 101 Bars Patents on Software”. To quote:
In Intellectual Ventures v. Symantec, [2015-1769, 2015-1770, 2015-1771] (September 30, 2016), the Federal Circuit affirmed summary judgment that the asserted claims of the ‘050 and ‘142 patents were directed to ineligible subject matter and reversed the finding that the asserted claim of the ‘610 patent covered eligible subject matter.
At Step I of the Mayo/Alice Test for the ‘050, the Federal Circuit agreed that the ‘050 patent was directed to the abstract idea of filtering emails, noting that it it was long-prevalent practice for people receiving paper mail to look at an envelope and discard certain letters, without opening them, from sources from which they did not wish to receive mail based on characteristics of the mail. At Step II of the Mayo/Alice Test, the Federal Circuit rejected the argument that because the jury determined that the prior art did not anticipate or make obvious the claimed invention, the claims necessarily met Step II, noting the fact that the claims may not have been anticipated or obvious does not suggest that the idea of “determining” and “outputting” is not abstract, much less that its implementation is not routine and conventional.
All other law firms seem to be looking at other cases, as if the above never happened or isn’t worth covering. This serves to confirm what we have been saying about cherry-picking. The following article by Matthew A. Ambros of Foley & Lardner [1, 2] is an example of misdirection and here is another example of it. From Joseph Robinson and Robert Schaffer came another distracting piece, leaving in tact only the aforementioned attack on the judge (courtesy of Watchtroll himself).
Another utterly misleading bunch of articles whose authors live 3-4 weeks in the past (McRO) and ignore the latest case can be found in [1, 2] or the repeatedly bumped-up (in the news) “Federal Circuit Strengthens Software, Business Method Patents” (behind paywall). One might get the impression from these that software patents are doing great, enjoying a resurgence, etc.
It is absolutely amazing that no legal firm that profits from patents (except from the one example above) speaks about the latest major case at CAFC. They talk about all sort of other things that serve to distract their clients. Covering another case (old case, new article), this one speaks about program running on a general-purpose mobile phone not being patentable. Like that wasn’t already obvious…
Sob Stories
Last week the Wall Street-centric media posted a pro-patents sob story/puff piece. “Patents for diagnostic methods and natural products have become difficult to obtain of late, although the U.S. law in this area is still evolving,” the author stated.
They are speaking for monopolies, not for ordinary businesses. So did Mark Summerfield, who quit his job last month and openly asked Watchtroll for some kind of attack piece on the judge. To quote: “Looking forward to your excoriation of Mayer’s appalling concurring opinion in IV v Symantec. I assume it’s on the way?”
Well, personal attacks are Watchtroll's expertise. We wrote about this a couple of times on Tuesday, expecting some ad hominem attacks from the ‘usual suspects’ and we were right. Henrion said, “if the watchdog would be serious about expropriation, the article would not be about defending patents hein…”
“I can’t speak for Gene, but I care more about my clients than money,” Summerfield wrote, “which is why I just quit my job” (citing his blog post about it).
Speaking to others (Crouch in this case), Henrion said about SCOTUS refusing to revisit software patentability that it’s “another way to say to the patent community if they got the message in the first place?”
Mikko Hypponen, writing about the latest ruling, said: “I can’t wait for software patents to die. And I hold several software patents myself.”
“Writing software is hard,” Daniel Nazer (EFF) wrote. “Having a vague idea about software is easy. Software patents reward the latter and punish the former. End them.”
“If copyrights were adequate,” Henrion said, “why does Red hat so closely associated [sic] with OSS have so many hundreds of patents?”
We actually wrote about this several times in the past.
Linking to this item, one patent attorney wrote that “Uber Has a Big Alice Problem,” as if anyone out there should care about an evil company like Uber and sob for it.
We expect many pieces in the corporate media in the coming weeks, explaining why the CAFC’s ruling has dealt a blow to “innovation” or some other myths. We can envision that such pieces would be composed by large corporations, their patent lawyers, or journalists who sparingly quote those two groups. █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
10.09.16
Posted in America, Patents at 6:12 pm by Dr. Roy Schestowitz

Summary: Texas and its epidemic of patent trolls (owing to trolls-friendly courts) may be enjoying its last months of exploitation and the patent law firms that are based there might soon need to relocate
THE USPTO is moving in the opposite direction of the EPO (which pursues the UPC). Tomorrow we’ll publish a lengthy and detailed post about the FTC study, but today — in preparation for that — we shall remark on another aspect.
A recent article by Annalee Newitz spoke about Lee Cheng, who made a name for himself by fighting patent trolls to death and even compelling them to pay Newegg’s legal fees after the trolls had lost (a lengthy and expensive process). Newegg was praised here in the past for this (one example among half a dozen from last year) and ““Patents are bullshit,” says Newegg legal chief” is the headline of this new article. To quote from it:
Lee Cheng is one of the few attorneys to fight back against patent trolls and prevail. And at the latest Ars Live event, we talked to him about his most famous case, how people can fight patent trolls today, and what the future of patent abuse will look like in coming decades. His answers, as expected, were incredibly candid and hilarious.
In 2007, a patent troll known as Soverain had already gotten millions of dollars out of The Gap and Amazon for their online shopping cart patent when they hit Newegg with a suit. Cheng’s colleagues in the legal community said you’d better just pay up—this patent is legit. Cheng didn’t see it that way. Newegg had just reached a billion in sales, and he thought this piece of litigation would be the first of many lawsuits brought by companies that wanted a piece of Newegg’s success. And sure enough, soon after the shopping cart claim, Newegg was hit with patent claims on several aspects of online search. Cheng decided he wasn’t going to lie down and take it. He thought he could win on appeal if he could just make it through the courts in the Eastern District of Texas, where 40 percent of patent infringement claims are brought.
Remember that Newegg got dragged down to Texas, and notably the Eastern District of Texas, which is probably the world's most notorious (globally). It actually advertises its bias that favours litigants with abstract patents. That’s why many companies and trolls file their patent cases in there. On the fifth of October we saw United for Patent Reform stating that “85% of the 33 patent lawsuits filed today were filed by patent trolls. It’s time for Congress to take action to #fixpatents!”
How many of these were filed in Texas?
Patent Progress wrote that “The Eastern District of Texas Is Still Home for Patent Trolls” (also under the #fixpatents hashtag) and pointed to this new article from Mr. Levy (cross-posted at the Huffington Post). To quote some bits:
The year is mostly over, so I thought I would take a look and see what’s going on in the Eastern District of Texas. The Eastern District of Texas still has more patent cases filed there than any other district at 1,224. Some 794 (that’s about 8% of all patent cases) of those cases were assigned to Judge Rodney Gilstrap, in the Marshall Division — almost 10 times more than any judge outside the Eastern District. That’s more than twice as many as the entire District of Delaware (311 cases), even though most big companies are incorporated in Delaware.
In fact, Judge Gilstrap, a judge in a small town in Texas, is handling about as many patent cases as Delaware, California, Illinois, and New Jersey combined.
Marshall, Texas has a population of about 25,000 people. It has no major research facilities, no major industries, and has not produced any major innovations that I can identify. And yet it hosts more patent litigation than any other place in the country, by an order of magnitude.
I’m sure Marshall is a charming town with nice people, but there’s simply no reason for so much patent litigation to go through there. We might as well have patent litigation go through Bangor, Maine, where I went to high school. The town is about the same size, but it has better food and it’s near the coast. Bangor also has a modern airport and a life-size statue of Paul Bunyan.
Seriously, it’s obvious that something is wrong here, even if you don’t know the details. Patent trolls wouldn’t be flocking to a small town with no airport unless they had good reason.
And they do have good reason.
Levy is right to single out or point out Mr. Gilstrap for reasons that we covered here before. In another new article, this one from Patently-O, they alluded to the VENUE Act [1, 2] by suggesting change to patent venue and naming the VENUE Act explicitly:
Earlier this year, we presented some initial results of our study of what might happen if patent venue reform took place. Since then, Senator Flake (R-Az) introduced the VENUE Act of 2016, and last month, petitioners, led by a group including James Dabney and John Duffy, filed a petition for writ of certiori in the TC Heartland case in the Supreme Court. Amicus briefs are due October 17, 2016 and Kraft’s brief is due on November 16, 2016.
To support these deliberations, we examined the history of the patent venue law and presented some statistics about plaintiff venue preferences for the Eastern District (for even more statistics on this point see the new paper by Brian Love and James Yoon). Additionally, we empirically modeled both reforms by randomly selecting 939 cases from 2015, and making our best guess as to where cases would have been filed under the proposed rules, assuming they would have been filed at all. Since 2015, the overall number of patent cases has declined, about 20% YTD based on data from Lex Machina (4,216 cases by this time last year vs. 3,369 today). The Eastern District of Texas has made a number of changes and its share is also down from 44% in 2015, to 35% 2016 YTD (30% in 1Q, 36% in 2Q, and 38% in 3Q); the next closest district (Delaware) has seen about 9% of filings, based on data from Lex Machina.
After the FTC study that we shall mention separately it seems more likely that the VENUE Act will become a reality, or folded into an existing/prospective patent reform bill.
Speaking of patent trolls, even universities are feeding them now. Here is MIP sort of supporting the practice, as if weaponising universities that are funded by the public and turn into trolls that tax the same public is a good thing. No wonder MIP did this, with firms like McKool Smith as ‘company’; To quote: “The increase in university patent lawsuits in recent years and strategies for winning cases were among the issues discussed by presenters in the webcast “University Patent Licensing and Enforcement”, hosted by Managing IP in association with McKool Smith on September 26.”
These are euphemisms for what often boils down to trolling, if not direct then indirect, e.g. by passing patents to trolls like Intellectual Ventures — now at the epicentre of the collapse of software patents in the United States (more on that in an imminent long post as well).
If the VENUE Act passes, or even gets incorporated into a future patent reform bill, then Texas can say goodbye to a lot of its parasitic business. █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
Posted in Asia, Europe, Patents at 5:24 pm by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
Poor quality patents (SIPO) and lack of examination (INPI)
Summary: The trajectory of the EPO under Battistelli’s leadership gives cause for very serious concerns, which include patent trolling and a humongous disservice to existing grantees of EPs (European Patents)
THE EPO may be going down the road of both China's SIPO and France's INPI (where Battistelli and many of his cronies at today's EPO top-level management came from). The Chinese have remarkably low patent quality (quantity over quality is the mantra) and the French, who fail to attract applications (French is spoken by far fewer people than Mandarin speakers), hardly care about quality at all. A French INPI clerk just rubberstamps (or simply files/shelves) everything that comes in. If the EPO follows the French model, then no examiners will be needed, just clerks who can follow a simple manual. How would one feel about one’s old/er EP/s if every crappy application on the EPO’s pile was suddenly granted or at least given hasty consideration for the sake of so-called ‘production’? Battistelli’s policy poisons the well or muddies the water right now. It is unfair to people who spent a fortune (and many years) pursuing EPs.
“If the EPO follows the French model, then no examiners will be needed, just clerks who can follow a simple manual.”As we noted here several weeks ago, east Asia is becoming attractive to patent trolls [1, 2], due in part to low patent quality (same as was the case in the US). There are more trolls and litigation, not just poor patent quality; there’s a correlation between those two things. SIPO is by far the worst in that regard. Korea and Japan, in the mean time, recognise the self-destructive nature of M.A.D. with patents, based on another article from IAM that says: “This blog has noted that one of the big themes in Asia’s automaking industry this year has been a significant move by Japanese and Korean brands to join defensive patent alliances. It’s a strategic shift for the industry that in many ways is being led by companies in this part of the world, rather than their North American and European counterparts. But Chinese companies have not yet followed the same path in significant numbers, and industry observers say with litigation on the rise there, buy-in from players in China will be crucial for these alliances going forward.”
One or two of IAM’s paid (partly by patent trolls) writers have focused a lot on Asia recently. See the latest issue’s “Patents in Asia 2016″ series, including focus on China, Japan, South Korea, and Malaysia. The feature item was actually about China, titled “Putting China’s patent rise into context” (all behind a paywall) and Jacob later wrote (partly in relation to this) that China welcomes crappy patent applications from the US, just like the EPO under Battistelli does. He recently started following me in Twitter (maybe out of curiosity, I find him a lot more balanced than Mr. Lloyd and Mr. Wild) and he didn’t put it in these words but instead he wrote:
It was eye-opening, but not necessarily shocking, to read on this blog last Tuesday the suggestion that Huawei’s mobile patents might generate up to 20% of all the patent income earned by Chinese companies. The conjecture appeared in a new research paper which seeks to revise (downward) earlier estimates of the total royalty stack on the typical mobile phone. The study looked at 49 major mobile licensors, of which Huawei was one of only two Asian operating companies (the other being Samsung Electronics).
Credit the Shenzhen-based company for building an IP team that has put it head and shoulders above its domestic competitors in terms of patent portfolio strength. I was reminded, though, of a quote by Huawei head of IP Jason Ding that appears in the issue of IAM out this week…
There is also an article about Foxconn.
Asian companies haven’t much to gain from a crappy patent system. Take Samsung for example. The most stupid patent that has made headlines in recent years (slide-to-unlock, hardly a novel concept at all) might soon cost Samsung more than $0.1 billion, based on reports like this new one and some remarks from Florian Müller (he wrote a lot more about it in Twitter). To quote Bloomberg (cited by Slashdot):
Apple Inc. won an appeals court ruling that reinstates a patent-infringement verdict it won against Samsung Electronics Co., including for its slide-to-unlock feature for smartphones and tablets.
In an 8-3 ruling, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit said a three-judge panel was wrong to throw out the $119.6 million verdict in February. Instead, it ordered the trial judge to consider whether the judgment should be increased based on any intentional infringement by Samsung.
Does this not demonstrate how foolish software patents harm companies like Samsung, whose home country (Korea) does not permit software patenting (we wrote about this earlier in the month)? This new IAM article remarks on patent tax when it comes to phones, which makes them very expensive (“licensing return from mobile market at $14.3 billion”).
As for the patent system in France, where does one even begin? The patent system in France is worse than a bloody joke; one might even call it a facility for corruption in light of details about the Patent Boxes (we wrote about this too, several times in the recent past alone). Here is a new article about it, demonstrating that journalists have begun catching up with the dirty scheme:
France’s patent box legislation, which permits a 15 percent corporate tax rate for profits from licensing of intellectual property rights rather than the usual 35 percent corporate tax rate, is being challenged as unfair to the European Union single market.
The matter has come before the EU Code of Conduct Group for Business Taxation, where several EU countries—including Ireland, Bulgaria and the Baltic nations— are insisting the French patent box regime should be considered harmful.
Among those contesting France’s IP rate are EU member countries that were themselves previously criticized by France over their overall low corporate tax rates.
“The issue has surfaced because France insists its regime doesn’t need to be reformed as all EU member states agreed to do in 2014,” a European Union diplomat, who participates in the Code of Conduct Group of Business Taxation, told Bloomberg BNA Sept. 30.
“However, all other EU countries are reforming their tax regime and insist France must do the same. Some of these countries, many of them resentful over French criticism of tax dumping, are rejecting the French arguments against reform.”
In this new IAM article a connection between the French and the Chinese is highlighted, in the form of “France Brevets”:
Unlike IP Bridge and Intellectual Discovery, France Brevets did not provide comment for the feature, but anecdotal accounts suggest that there has been something of a shift in strategic focus at the firm in recent months – and the call for change has come from the highest levels.
It appears that securing a return on its 100% public sector investment is now the fund’s primary objective, with its aims of boosting the domestic SME sector and kickstarting a local market in IP assets taking a back seat, at least for the time being. Simultaneously, some key personnel have come and gone; in June, founding CEO Jean-Charles Hourcade was replaced by Didier Patry, who was previously head of IP at Eaton Aerospace and before that led Hewlett-Packard’s IP transactions department from 2002 to 2014. Pascal Asselot, who had served as the fund’s director of development and licensing since its establishment, departed in the same month.
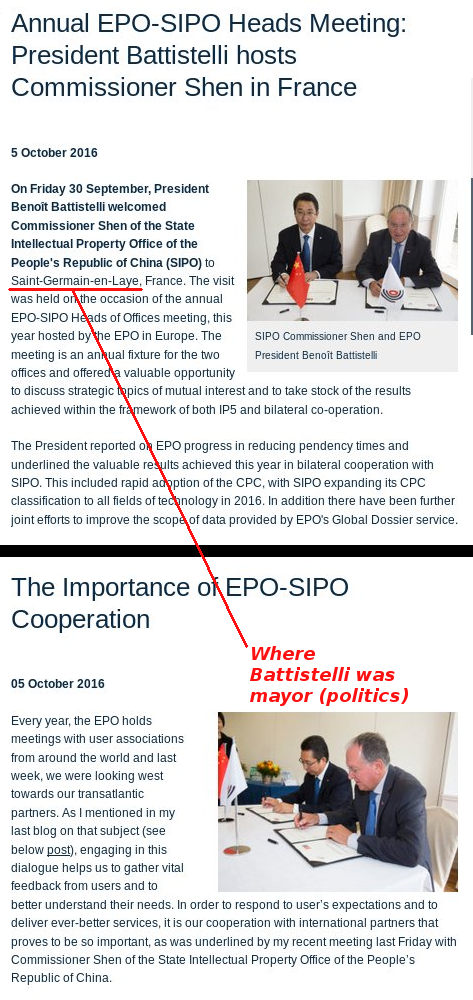
The USPTO, which finally tightens patent scope and goes after trolls (more on that in articles tonight and tomorrow), isn’t the world’s worst; some of the worst are probably SIPO and INPI and this is what the EPO is connecting to (several days ago Battistelli bragged about meeting SIPO officials in the town where he used to be a mayor, over in France that's not even an EPO host nation). █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
Posted in Europe, Patents at 3:41 pm by Dr. Roy Schestowitz

Summary: Suspicions that the popular blog IP Kat is suppressing criticism of the UPC are being aired, belatedly, over at IP Kat, hinting at the possibility of self-censorship due to financial motivations rather than fear of the EPO’s legal bullying, or strategic lawsuit against public participation (SLAPP)
THE EPO, as we last noted this afternoon, is trying to control not only media companies but also blogs, staff, and any other means of communication. The Office wants media blackout and information lockdown. Nobody but the chronic liar (Battistelli or cronies like Margot Fröhlinger) is allowed to have a voice. AMBA, for example, is too afraid/reluctant to even respond to E-mails from Managing IP. This is basically the current strategy of the EPO and in a sense it’s both clever and effective. That’s why North Korea and Iran adopted it.
Remember the times when IP Kat was a go-to place and a critical voice regarding the EPO? That was quite a while back. They write nothing about the subject anymore, so I asked them about it online. I am still waiting for an answer.
Several interesting (but old) comments were published at IP Kat shortly after we had noted something about IP Kat not publishing particular comments (we wrote about it in the afternoon), though the timing is quite possibly a coincidence, so we’re not suggesting that they did this in response to something we had written.
Here is what one comment asked: “Dear team of IPkat, I haven’t seen a post about the situation at the EPO since a couple of months. How come? Do you think there are no news? Have you been threatened? 3 staff rep in The Hague are being under investigation at the moment. Staff is planning demo next week. How come you do not report about it?”
No response since. I too asked them and have not received a response. “Has IP Kat been threatened — not just censored — by the EPO,” I asked IP Kat and its founder. “Given the circumstances, no reply might be “yes”,” I added.
Remember that IP Kat already received threats from other such bodies, as did a few other bloggers (not even big publishers and paid journalists).
Nowadays it feels like IP Kat writers, not wanting to have particular things mentioned, simply suppress particular things (censorship and also self-censorship). Some believe it’s done for fear that the EPO would censor them again (or maybe even send threatening letters as they did to me). Some bloggers did humorously insinuate that IP Kat was next on the EPO’s naughty list. First they were added to the censorship list (after they had done this to me), so is a threat of lawsuit next in line? Just the thought itself would be enough to gag (self-censor) IP Kat. It’s known as the Chilling Effect and next week — not fearing retaliation — we shall write about the chinchilla effect.
Here is a comment about alleged criminals at the top of the EPO. The EPO simply chooses call those who mention charges against them “defamation”. Here is the comment which is days old and IP Kat has not published until a relatively short while ago (I see publication time through my RSS feeds):
To further reinforce the narrative about defamation, VP3 sued the member of the board of appeal for in a German court – you may have read the outcome above (28/09): it appears that the Procurator dismissed the case recently.
Actually it was VP4 who tried to file a lawsuit in Germany.
His litigation track record is not so hot.
In January 2015 he apparently lost a defamation lawsuit in his home country:
http://techrights.org/2015/03/18/full-judgment-against-topic/
Now it seems that the German Procurator didn’t even consider it worthwhile opening proceedings against the person accused of defamation.
But don’t worry he still enjoys the favour of the Lord Protector of Eponia.
“Well,” the person later added. “my last comment about VP4 seems to have been suppressed.”
This comment too was suppressed (no way it was detected/identified as spam), so it looks like IP Kat hoped nobody would notice what had happened. I was already told, since almost a year ago by multiple people, that IP Kat had been deleting (not publishing is the equivalent of that) their comments. They deleted mine too. See this example and also this one (later they blamed the latter on spam filtering, but the former they just simply deleted).
For IP Kat to suppress discussions about EPO’s scandals is a lot easier these days; now the blog just no longer writes anything on the topic (hence every comment would be off topic); the only comments about it (if published at all) are clustered in some very distant page from 4 months ago. “I think it is still possible to post,” one person wrote, but there’s no guarantee that what gets posted will in fact be published. Well, maybe it depends on what it’s about. Selective publication of comments is a form of censorship, by definition (I have been reading and writing about the subject of censorship for several years, so I am very familiar with the methods).
One person asked “Has the thread reached its limit” and “It seems so” was the response, until IP Kat suddenly published half a dozen comments in this thread alone (in the mean time it did publish numerous other comments, every day in fact, so being absent from moderation is not a valid excuse).
Please note, based on the above, that there are no offensive words in there or anything that should invoke a spam filter (potential excuse in these cases). There are no clickable links, either.
Another new comment, this one regarding the UPC which the blog habitually promotes/markets, says the site “seems to be so highly unwilling to put information like this in the public domain” because it’s against the UPC. The thread touches on (promotes) the UPC, so the comment is relevant, it’s definitely on topic, and it refutes the original propaganda from the Bristows employee by stating:
This is my second attempt to get this comment posted, after the first one made on 10/06/16 at around 11:30 a.m. CEST still remains to be published, despite its receipt having been confirmed.
To the commentators on 10/04/16, 21:13 and on 10/05/16, 8:30:
Don´t forget to mention Mr Haft who is also a member of said committee of the German Bar Association. His firm Hoyng ROKH Monegier was created just recently by a Dutch and a German firm joining forces in joyful anticipation of the UPC. Should the UPC now not become a reality, this may well consitute a delicate situation for them… It is vested interests like these that bring about desperate suggestions such as going ahead with the UPC at any cost and even without a crucial participant like the UK.
It is left to the imagination of the readers why the IPKat (and more specifically the author of this post) seems to be so highly unwilling to put information like this in the public domain, apparently going so far as to even censor respective comments.
These conflicts of interest in the collusion behind UPC 'experts' were previously noted in relation to Tilmann, whom we mentioned here before in [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]. This seems to suggest that the IP Kat blog not only censors criticism of the EPO but not also expands its suppression of comments to the UPC (although evidence is too scarce at this stage).
If IP Kat deleted (or did not publish) your comment/s, please get in touch with us so that we’ll know how broad the problem has become. If we are seeing selective coverage of particular sides depending on one’s agenda/goals/objectives/profit motive, then it is more severe than censorship and self-censorship for fear of SLAPP from the EPO.
For the record, Techrights accepted each and every one of the 33,583 comments posted over the years (zero censorship), including extremely rude and racist comments. That is what free speech means. █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend























 Content is available under CC-BY-SA
Content is available under CC-BY-SA