12.26.16
Posted in America, LG, Microsoft, Patents, Samsung at 2:35 pm by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
Scientists as judges, not just as pressured (from above) examiners

David Ruschke’s ‘official’ photo
Summary: The Patent Trial and Appeal Board (PTAB), led by David Ruschke, continues to function as another ‘layer’ that ensures patent quality by weeding out bad patents and here are some of the latest cases
THE patents and litigation climate is rapidly changing in the US. It’s not just about software patents, but it has a lot to do with them as a lot of litigation emanates from such patents, notably troll litigation.
Just before the days of the holiday (whichever one) we learned about the Patent Trial and Appeal Board (PTAB), which is responsible for invalidating many software patents, being in the midst of this battle:
The Patent Trial and Appeal Board announced on Dec. 2 that it would uphold a patent filed by Securus Technologies, and that the challenge filed by rival company Global Tel*Link (GTL) was invalid. GTL maintains, however, that Securus only won a partial victory.
The patent (U. S. Patent No. 7,494,061 B2) that Securus maintains held up to the challenge from GTL, relates to biometric identity verification monitoring devices used in correctional facilities. According to a summary of the patent, “The term “biometrics” refers to technologies that measure and analyze human characteristics for authentication.”
This patent is a software patent by the sound of it. These are actually the sorts of patents which improperly use terms like “biometrics” to sound as though they’re anything but image analysis, which is my field of research (post-doctoral). It has nothing to do with biology and it’s all typically reducible to mathematics (matrices). Does the appeal board (PTAB) realise this? If not, maybe it’s time to reassess.
Another report, last Updated 6 days ago, is an article about appeals in Korea, published by Jay (Young-June) Yang, Duck Soon CHANG and Seung-Chan EOM from Kim & Chang (patent microcosm). Remember that Korea still blocks software patents (as it should) and we commend this decision, which guards software giants (also hardware giants, not to mention military equipment players) like Samsung and LG — both of which became Microsoft prey for using Linux nearly 9 years ago. We last reported on this 3 months ago (Microsoft wants more 'Linux patent tax' in Korea).
Going back to PTAB, there is a CAFC/PTAB case (CAFC having the authority to object) that MIP explained as follows: “The original Federal Circuit panel decision in the case – written by Judge Reyna and joined by Chief Judge Prost and Judge Stark – was issued on May 25. The court affirmed the Board’s denial of Aqua’s motion to substitute claims 22–24 of a patent concerning automated swimming pool cleaners.”
There is a 9-page PDF in there. As mentioned here some days ago, they are complaining because their patent was granted in error and now they want to change it. Imagine if granted patents were something dynamic you could just amend, edit, expand etc. as you go alone. What a ludicrous thing. Invalidate the patent and if they insist it’s not fair, then they should apply for the patent again (with amended claims).
MIP also explains how to use PTAB to squash bad patents (like software patents) even when it’s not so trivial. “Jim Brogan, Brian Eutermoser and Janna Fischer discuss the ways that the unsuccessful IPR petitioner at the Patent Trial and Appeal Board still can challenge validity in subsequent district court litigation,” MIP wrote.
MIP, to its credit, keeps abreast of PTAB cases (mostly because of Mr. Michael Loney), although it sometimes misinterprets the numbers it puts forth.
In better news about PTAB, here is PTAB having a go at software patents and getting a chance to kill them again. As PatentDocs put it:
Petitioner, iVenture Card Traveler Ltd, filed a Petition seeking to institute a covered business method patent review of all claims of U.S. Patent No. 7,765,128, owned by Smart Destinations, Inc. The Board, applying the standard that requires demonstration that more likely than not Petitioner would prevail with respect to at least one challenged claim, the Board granted Petitioner’s request to institute the CBM review.
We hope that PTAB will continue to do its job improving patent certainty by knocking out a lot of rubbish patents, leaving in tact only those that merit court cases (if any). █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
12.22.16
Posted in America, Free/Libre Software, Patents at 9:44 am by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
 Summary: Innovations associated with Bitcoin/Blockchain — advancements which are largely Free/Open Source software-centric — are under threat from financial giants that effectively besiege/threaten startups using a barrage of software patents
Summary: Innovations associated with Bitcoin/Blockchain — advancements which are largely Free/Open Source software-centric — are under threat from financial giants that effectively besiege/threaten startups using a barrage of software patents
THE USPTO insists that it makes the US more competitive, but in many cases it actually helps large companies undermine small ones, not foreign ones.
Case of point: see the new article “When a patent-happy industry meets open-source technology” [1, 2]. To quote from the article:
When the financial services industry started paying attention to blockchain technology, many companies, seemingly as a reflex, sought patent protection for their ideas.
It was ironic, since the original bitcoin blockchain was a breakthrough of open-source development, in which software code is made freely available for anyone to use or modify. As the industry has gained a clearer understanding of how distributed-ledger technology could change its business, it’s begun to see the merits of such openness in supporting collaborative innovation, and the limitations of the traditional, you-can’t-touch-this approach.
Some are even using a hybrid strategy, pursuing patents to secure a competitive advantage – or at least protect themselves from legal challenges – while publishing code and inviting others to improve it by submitting fixes or patching bugs. The situation underscores the cultural differences between the banking and technology fields as the former looks to the latter for help meeting the demands of an increasingly digital world.
IBM’s Manny Schecter was interested in this and Benjamin Henrion told him that these conglomerates pursuing patents on Blockchain technologies is “like oil companies patenting everything solar.”
This isn’t entirely new a revelation. It’s an old trick in many industries (absorbing or denying competition that suggests alternative paradigms). Big Banks are essentially attacking Bitcoin, Blockchain etc. using software patents and today we found two more articles about it, “Blockchain patent filings by Goldman, others tip future cost risk” and “Corporate Patents on Blockchain Could Create Legal Problems for Startups”. Well, that’s the intention.
“Thankfully, a lot of software patents pertaining to payments and finance are being invalidated these days (thrown our by court), more so than in any other field.”“Over the past few months,” one of these articles says, “some of the world’s largest financial companies including Goldman Sachs, Bank of America and Mastercard – have been patenting promising Blockchain methodologies. Despite a common perception that Blockchain is Open Source and developers can freely use Sotoshi Nakamoto’s ideas from bitcoin to build new systems, it still could mean costly legal problems for fledgling startups, lawyers and others are saying.”
We wrote about this not too long ago in relation to MasterCard. A lot of the above culminated in the publication of “Big Banks Are Stocking Up on Blockchain Patents” (early yesterday in Wall Street media). To quote:
In the headlong rush to revolutionize modern finance, blockchain enthusiasts are overlooking one potentially costly problem: their applications, built on open-source code, may actually belong to someone else.
Recently, some of the biggest names in business, from Goldman Sachs to Bank of America and Mastercard, have quietly patented some of the most promising blockchain technologies for themselves. Through mid-November, the number of patents that companies have obtained or said they’ve applied for has roughly doubled since the start of the year, according to law firm Reed Smith.
Our readers are smart enough to know what’s wrong with this picture. Gullible people may try to frame this as a sign of “adoption” and “success”, but the large financial firms just want to guard their monopoly/oligopoly, they don’t want disruption.
Thankfully, a lot of software patents pertaining to payments and finance are being invalidated these days (thrown out by courts), more so than in any other field (about 90% of the time). That’s similar to business methods, too.
Are patent examiners in the US paying any attention at all to what courts have been arguing over and over again? █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
12.21.16
Posted in America, Asia, Deception, GNU/Linux, Microsoft, Patents at 8:39 am by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
Scare tactics and vengefulness from the Patent Maximalists’ Lobby
Summary: The growing embrace of “China” as the convenient bogeyman for those who oppose patent reform and wish to see a resurgence of patent chaos, from which they personally profit at victims’ expense
THE USPTO may be in self-perpetuating denial about it, but software patents are a dying breed in the US as courts don’t tolerate them. The EPO, in the mean time, moves in the opposite direction, but we’ll leave the EPO out of this post’s scope.
Unhappy With Insufficient Number of Lawsuits and Collateral Damage
Paul Morinville, a prominent opposer of patent reform in the US (and part of Watchtroll’s ilk), whines that “PTAB procedures are now invalidating nearly 90% of all patents they evaluate.” Yes, so what? Alice and other cases are pretty clear about it and PTAB, unlike patent examiners, is not being pressured to just bless every patent in the name of “production” or “success” (again, a growing problem at today’s EPO).
Morinville picks on Google (large company as his latest scapegoat) and some of his online friends already heckle me for pointing that out. To quote his article: “Over the next decade, the Supreme Court would eliminate injunctive relief and then for all intents and purposes, invalidate their patents first under Bilski and then under Alice. The courts also changed the way claims were written, thus invalidating thousands of patents retroactively. The America Invents Act’s PTAB procedures are now invalidating nearly 90% of all patents they evaluate. The courts also radically reduced damages for patent infringement.”
That’s good. But wait until Morinville brings up the bogeyman again — the same bogeyman that David Kappos has been summoning recently.
Let’s Envy China
“With China strengthening its patent system,” Morinville says, in probably the most ludicrous part of the whole article. China is actually weakening patents by granting almost everything that comes through SIPO’s doors, causing a patent hyper-inflation and an epidemic of trolling. How is that desirable to anyone but the patent microcosm? These anti-AIA think tanks and lobbyists (like Morinville), who want more lawsuits and more litigation, continue to infest the Web and a lot of them congregate around Watchtroll these days. This pattern of China-blaming or China-shaming mirrors what the Democratic Party in the US has been doing with Russia as of late.
Watchtroll wants the USPTO and the courts to start another race to the bottom and give/approve patents on everything, just like SIPO in China. One might call it “the litigation lobby” — for all it want is more and more lawsuits (which the lobby profits from). Watch another new Watchtroll article, this time by Steve Brachmann, the henchman of Quinn. So people who don’t even develop anything insist that “China” is the threat and that “Chinese patent guidelines” are a threat to the US rather than to China itself.
What kind of post-truth nonsense have we sunk to here?
Watchtroll, in another new article, says “Keep it Cordial” while Quinn attacks everyone who does not agree with him, even judges (see the image at the top).
What a nasty Web site this is. For IBM’s patent chief to occasionally link to it probably takes some guts because it says a lot about IBM, which has gone rogue (even IBM employees now protest/object to the management over that infamous Trump fawning).
China’s Growing Trolls Epidemic
China’s situation with regards to patents is not good. As we have been pointing out since the summer, SIPO grants far too many patents, including software patents. “This is especially true for software patents where the scope of patent protection is rather vague,” says this new article from China, which also mentions Xiaomi, a company that got trolled through India, as we noted before. To quote the relevant part:
As Chinese smartphone brands work to carve out a spot in the major-league global smartphone industry, they are increasingly being dragged into an international patent war with foreign tech firms.
The latest case saw San Francisco-based audio tech firm Dolby Laboratories lodge a lawsuit against Chinese smartphone companies Oppo and Vivo in India, accusing them of infringing on its patented technology. Back in 2014, Chinese tech firm Xiaomi was barred from selling phones in India after Sweden-based Ericsson filed a complaint with an India court alleging patent infringement.
The Ericsson-Microsoft patent trolls strategy (using trolls as proxies) was mentioned here twice this month [1, 2] and Xiaomi is again being mentioned by the Microsoft Windows-powered IAM (with other Microsoft connections). It is again embellishing Microsoft's patent extortion against Linux as follows:
The May agreement between Microsoft and Xiaomi was undoubtedly the IP deal of the year and it was also an excellent example of how patents can play a role in broader commercial agreements. Under the terms of the deal, Xiaomi undertook to pre-load Microsoft products on to more of its mobile devices, the two sides agreed to a cross-licence and the US software giant transferred 1,500 patent assets to the Chinese company. The transaction provides an excellent foundation for Xiaomi as it looks to grow its business in the US and for Microsoft as it continues its penetration of the Chinese market.
This is misleading. All we have here is patent extortion by Microsoft against Linux, even in China where the government of China took a strong stance against it (even leaking a list of Microsoft patents that are secretly being sued to blackmail Chinese companies like ZTE). We believe that Huawei, the world’s leading Android OEM these days, is still able to resist Microsoft’s Mafia-like tactics. Microsoft repeatedly failed to sign a patent deal.
The bottom line is, China has become a dangerous place patents-wise. Is that desirable to anyone but the patent microcosm? Of course not. █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
Posted in America, Patents at 8:16 am by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
Because protectionism alone does not breed creativity and innovation

Summary: Signs that the patent system is on the one hand improving, thanks to the Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS), but on the other hand it continues to deny choices in the market by altogether blocking products
THE Justices of SCOTUS may soon be ending patent trolls' business model, irrespective of patent scope restrictions (like Alice at SCOTUS), which USPTO barely cares to respect anyway (it’s left for courts to do the job that USPTO examiners fail to do). As one new article puts it: “In a move that may shake-up U.S. patent law, the Supreme Court this week decided to hear a case about where patent owners can file lawsuits—a case that will likely put an end to a special Texas cottage industry that has been a thorn in the side of big business.”
Not just “big business”. In fact, that mischaracterises the entire problem because big businesses can usually afford going to court where they challenge the trolls. Small businesses cannot afford to do this and they suffer the most, usually quietly (under gag orders/instructions upon settlement).
Who does the current patent law work for best if not big businesses? Merck recently got awarded 2.5 billion dollars in supposed 'damages' in one single case. Who lost this patent case? Poor people who will die as a result of lowered/no access to drugs. As a medical news site put it the other day: “A federal jury awarded $2.54 billion in royalties to Merck, which owns the patents that Gilead allegedly infringed upon to create its two blockbuster hep C drugs, Sovaldi and Harvoni.”
So Merck not only gets a lot of money but also maintains a monopoly that will enable Merck to further jack up prices. Who benefits from this?
Another item of news deals with the ITC‘s decision to block Arista products — a subject on which we wrote in the past [1, 2]. MIP says the following about the latest twist:
The ITC’s ruling, administered by Judge Mary Joan McNamara, found that Arista had imported into the US two components for routers and networking systems that infringe upon Cisco’s patents, in violation of Section 337 of the Tariff Act. Arista plans to request a full review by the Commission, according to its press release.
As we pointed out before, when denying sales of Arista products those who suffer the most are ordinary people, not just Arista employees (the smaller company). Getting the patent system in tune with or in alignment with public interests is crucial. Otherwise people will simply cease to respect patent law — in the same way (and for similar reasons) a lot of people already regard copyright law to be tilted in favour of conglomerates and non-producers. █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
12.19.16
Posted in America, Courtroom, Europe, Patents at 6:34 pm by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
Summary: Short roundup of news regarding patents in the United States and the process of handling them, with few comparisons to the EPO
LITIGATION with USPTO patents is down. It is down pretty sharply and this gives ample room for hope. But it does not, however, mean we should take our eyes off the ball.
Patently-O, writing in another recent post, said that “Medgraph’s claims are directed to a set of methods “for improving and facilitating diagnosis and treatment of patients.” See U.S. Patent 5,974,124 and U.S. Patent 6,122,351. The problem is that the claims require actions by both the computer system and also a patient/doctor. This claim structure directly runs headlong into traditional requirement for direct infringement of a patent – that all steps of the claim be performed-by or attributable-to a single entity.”
What’s noteworthy here is the presence of a computer system. We previously wrote about a similar case at the EPO appeal boards (computer conjoined with “medical” and “device” so as to make it look/sound non-abstract and novel). Right now in Europe it’s said to be easier to get (and defend) software patents than it is in the post-Alice US. The judge in the above case, P. Corcoran, thankfully rejected the application. No wonder Battistelli hates the appeal boards so much and strives to destroy them (while still maintaining the appearance or perception he complies with the EPC).
In other news from around the Web, there are formal/procedural changes emanating from CAFC decisions. “A recent decision from the Federal Circuit recognises a privilege between non-attorneys patent-agents and their clients under certain conditions,” says MIP. “Philippe Signore reviews the limits of this patent agent privilege, as well as those of the attorney-client privilege, within the context of the discovery phase of a US litigation,” continues the summary, but the article is behind a paywall.
“Federal Rule of Civil Procedure 6 has,” according to this from Patently-O, “since it first allowed for service by electronic means [legal papers served by E-mail, as the EPO attempted to do to me], treated it like other means of service, adding 3 days to the deadline to respond (under some circumstances). It’s now been deleted from the types of service that give the extra there days.”
Writing about a CAFC case, Patently-O also mentioned that “Patent Nos. 6,107,851 and 6,249,876 were not anticipated and were directly and indirectly infringed by Fairchild and that Fairchild’s Patent No. 7,259,972 was not obvious and was infringed by Power Integrations under the doctrine of equivalents (but was not literally infringed or indirectly infringed by Power Integrations). The jury also found Power Integrations’ Patent No. 7,834,605 neither anticipated nor obvious. Following trial, the district court granted judgment as a matter of law that Fairchild directly infringed this patent. The district court granted a permanent injunction against Fairchild and declined to grant an inunction against Power Integrations.”
The term injunction is just a nicer word for embargo and when companies start banning/blocking each other’s products it’s clear who’s not winning: the public. █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
Posted in America, Patents at 6:18 pm by Dr. Roy Schestowitz

Source: 2013 interview
Summary: In spite of repeated rejections of software patents by high courts in the United States, those who profit from such patents carry on as if nothing happened and even pay the former Director of the USPTO (David Kappos, pictured above) for lobbying
NOW THAT it’s publicly being stated that the EPO is more software patents-friendly than the USPTO (in spite of the ban; not that Battistelli minds any laws whatsoever) we thought it would be a good time to bring up this new press release that says “Samesurf [...] announces the issuance by the USPTO of five patents relating to co-browsing and synchronized browsing of online content: (1) US Patent No. 8,527,591; (2) US Patent No. 9,171,087; (3) US Patent No. 9,185,145; (4) US Patent No. 9,483,448; and (5) US Patent No. 9,489,353.”
These are of course software patents, so one has to wonder if the USPTO dealt with old applications as though the new rules (Section 101 and whatnot) don’t apply. Of course not, but something is rotten here and it’s very improbable that a high court would accept these patents upon closer examination. After Alice it barely matters if the USPTO puts some stamp on this stuff; courts and appeal boards would likely undo the stamp (it asked/petitioned to do so). So what is Samesurf bragging about really?
Suffice to say, the USPTO still wants to just grant a whole lot of nonsense. It makes the USPTO look “productive” and they probably just label it all “innovation”. Recall the latest echo chamber of the USPTO (not the first of its kind) that promotes software patents and excludes actual software developers. The patent microcosm, which opposes Alice (obviously!), publishes this new article, soon thereafter to be predictably promoted by proponents of software patents including IBM’s patent chief. To quote the key parts:
Section 101 patentability challenges of the 1970’s, in Benson and Flook, culminated in the Diamond v. Diehr decision of 1981, and the roughly contemporaneous Chakrabarty decision of 1980, set out an admirably broad ambit for patentability on the advent of the digital and biotechnological revolutions that have transformed our world these last 35 years. Coming as they did at the foundation of the Federal Circuit, these decisions reinforced a view that the US patent system was capable of broadly encompassing “anything under the sun that is made by man,” the Chakrabarty Court quoting the Senate Committee report on the 1952 Patent Act.
[...]
To address this situation through legislation, I suggest something along the lines of adding a straightforward sentence at the end of Section 101:
101. Inventions patentable. Whoever invents or discovers any new and useful process, machine, manufacture, or composition of matter, or any new and useful improvement thereof, may obtain a patent therefor, subject to the conditions and requirements of this title. For purposes of this section, it is irrelevant whether the invention or any of its claimed elements, is otherwise unpatentable under sections 102, 103 or 112.
I believe something this simple, or its equivalent, accompanied by clear legislative history, could help undo so much of the new troubling jurisprudence that imports these other conditions of patentability at the outset, and restore 101 to the minimal, simple threshold for inventions of the useful arts to which it was always intended.
The patent microcosm is trying to change the law and even the former Director of the USPTO was recruited for this task. They just want more and more patents on everything and lower quality control, obviously.
Don’t lose sight of these people. Their malicious agenda is a detriment to software development. They don’t even develop any software. █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
Posted in America, Patents at 5:20 pm by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
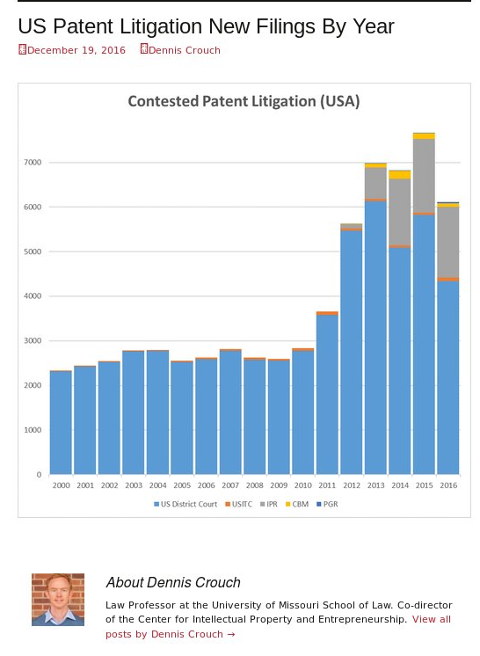
Credit: Patently-O
Summary: The United States sees a decline in litigious activity as Alice sets in and devalues software patents (which many frivolous patent lawsuits have been about)
THE chart above, produced and published without comment by Patently-O earlier today, helps confirm that litigation was (still is) down sharply this year. Good news for everyone but the patent microcosm and patent trolls, right? It does not yet make Crouch’s job irrelevant.
We previously remarked on this trend, based on similar data that demonstrated sharp decline in litigation. Many people attribute this to Alice and Mayo. █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
12.18.16
Posted in America, Google, Patents at 6:16 pm by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
Ignore the old and tired myth of large businesses ‘stealing’ ideas of the ‘little guy’…
“Small enterprises generally adopt a rather negative position towards the current increasing granting of patents for software and algorithms because they fear that these will hamper or eventually even impede their work (more than 85%).” —German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), Study of the Innovation Performance of German Software Companies, 2006, p. 86
Summary: The US patent system helps discrimination against small businesses or family-owned businesses — a problem which is likely to exacerbate/deepen under the next administration
THE USPTO has long been run by people from big industry and big companies. Watch what David Kappos has turned into. It remains to be seen where Lee will go after her time at the Office (Trump will pursue her removal, with high level of certainty).
Timothy B. Lee, a critic of software patents for about a decade now, has this new article about Trump in which he says “Google [is] also advocating reforms to rein in low-quality software patents” (we wrote about this the other day). Here is the key part:
In recent years, Google and Microsoft have both been actively lobbying for patent reforms to rein in litigious patent trolls, with Google also advocating reforms to rein in low-quality software patents. Trump will not only choose a new director for the patent office, he will also have influence over patent reform legislation over the next four years.
What about the views of small companies? As many people have already pointed out, Trump seems to be giving his ears only to billionaires and companies that rake in billions. It’s oligarchy on steroids. And watch this truly terrible advice from a truly terrible news site that famously glorifies billionaires. Big corporations’ media is now misleading small businesses on software patents by saying:
Why Patents Should Be Part Of Every Startup’s Risk Mitigation Strategy
[...]
The debate over whether software should be patented goes back to the beginning of software, but a good example is looking back to when Microsoft was a young company with almost no patents. Now they are one of the most prolific patent filers.
Actually, to quote Microsoft’s chief at the time, “[i]f people had understood how patents would be granted when most of today’s ideas were invented, and had taken out patents, the industry would be at a complete standstill today.”
Gates, who actually said that, complained that patents were harmful to small companies (like his at the time). Why pretend that, as Forbes put it, “Perhaps somewhat surprisingly, companies in industries that are seeing some of the most rapid innovation — like software and tech companies, particularly those focused on content delivery — often ignore the problem and don’t focus on future risk mitigation until they have a problem, and the result can be costly” (they actually cite Watchtroll!!!).
What they mean by “risk mitigation” is pursing patents of their own. What a terrible advice.
See this new article titled “The biggest threats to the free web” whose first section is “Software Patents”. To quote:
No one can own the web, but many companies are attempting to slice it up and own the very concepts that form the web. Software patents, unlike standard patents for inventions, do not actually involve the creation of tangible objects. Instead the U.S. patent office has handed out patents for ideas like the double-click or the use of a single button to make a purchase.
While the European Union has taken a more aggressive stance against software patents, the U.S. is now entangled in them with major companies like Google and Apple battling it out through proxy lawsuits. One firm, Eolas Technologies, claims to own the patent for the “interactive web” and threatens to undermine the very freedom of the web itself.
As history shows, and basically throughout the whole history of patents, the system was used as a mechanism of protectionism. Large companies used it to keep small companies from being able (or allowed) to compete. Why pretend that any of this has changed? And moreover, why on Earth cite propaganda from Watchtroll in an effort to urge small companies to hop on the patent bandwagon? It is widely known that for small companies to read patents only makes them more vulnerable (willfulness of infringement), patent applications make them poorer and enforcement of patents against trolls is impossible; enforcing patents against giants like IBM is worse than stupid because IBM can then retaliate with far more patents, so it’s not hard to see who this system really serves (by design, by persistent lobbying). █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
« Previous Page — « Previous entries « Previous Page · Next Page » Next entries » — Next Page »


 Summary: Innovations associated with Bitcoin/Blockchain — advancements which are largely Free/Open Source software-centric — are under threat from financial giants that effectively besiege/threaten startups using a barrage of software patents
Summary: Innovations associated with Bitcoin/Blockchain — advancements which are largely Free/Open Source software-centric — are under threat from financial giants that effectively besiege/threaten startups using a barrage of software patents



















 Content is available under CC-BY-SA
Content is available under CC-BY-SA