01.08.17
Posted in America, Asia, Microsoft, Patents at 3:53 pm by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
Hiding behind fronts, attack dogs, and interest groups

Summary: A potpourri of reports about some of the world’s worst patent trolls and their highly damaging enablers/facilitators, including Microsoft which claims that it “loves Linux” whilst attacking it with patents by proxy
THE ISSUE associated with patents as a ‘pure’ business model, or patent trolling, is widely understood. Imagine a world where people profit from making nothing at all, just demanding money from (if not blackmailing) companies that make actual sales and have a source of income/revenue, namely customers that buy products.
More patent trolls news came from the trolls-funded IAM the other day. “According to a December 29th release,” it quoted, ““Fortress will have the sole discretion to make any and all decisions relating to the company’s patents and patent monetisation activities.” Inventergy has around 740 patent assets acquired from Nokia, Huawei and Panasonic in a series of three separate deals in the first half of 2014.”
Here again we see Nokia as trolls’ ammunition, just like at MOSAID (now known as Conversant, which pays IAM’s publisher). Speaking of MOSAID, which Boris Teksler is involved in (hopping between Microsoft-connected trolls), see this new list from IAM. The Editor in Chief of IAM gives him (yet again!) some special honour, without noting that his employer paid IAM (under the new name, Conversant). So much publicity for an aggressive firm (actually a patent troll) from IAM… one might begin to think that it’s coverage that money simply buys. Conversant is such an evil patent troll (working for Microsoft’s interests now) that it had to change its name and now it’s trying to improve its reputation with some puff pieces? And from who, from IAM? Watch this latest IAM revisionism about Xiaomi (yet again!), maybe for the third time in the past month alone. We already explained that Microsoft was extorting Xiaomi with patents, but IAM tells a sanitised, face-saving PR story for Microsoft:
Xiaomi – Who says the IP deals market is flat? During 2016, Chinese mobile manufacturer Xiaomi – not yet 10 years old – seemed to be on a one company mission to prove that this is far from the case. In January it emerged that it had got its hands on a suite of Broadcom patents while a month later came the news that it had acquired a significant portfolio of US assets from Intel. Both deals, though, were eclipsed by the ground-breaking transaction with Microsoft announced at the end of May – a win-win for both that exemplified the way that IP is now forming the bedrock of much wider co-operative agreements between operating companies. While all this was happening. Xiaomi was also incorporating Zhigu Holdings into its internal operation – a move that saw the aggregator’s president and chief operating officer Paul Lin become Xiaomi’s VP of IP strategy. That could well prove to be a masterstroke, with Lin having gained a great deal of deal-making experience at both Intellectual Ventures and Microsoft while based in the US. Like many young Chinese technology businesses, Xiaomi is running a significant patent deficit; but unlike many of them it has recognised it needs to be aggressive in doing something about this. To expand, it will not only have to develop its own IP, but must continue to be active and creative in bringing it in form third parties. With Lin enjoying enlightened support from the very top of the company, Xiaomi is set to become an even bigger patent player in 2017.
Notice the connection between “Intellectual Ventures and Microsoft” (in the above text). It’s a strong and well established connection, which we have been covering for nearly a decade now. Microsoft uses the world’s largest patent troll, which it itself created/funded, to attack Linux. It’s a common tactic where the troll is mostly/only a proxy.
Similarly, as mentioned here the other day, Faraday Future throws its patents at some shell company and this new article from TechDirt looks deeper at the anatomy of it:
That’s all interesting… but what’s amazing is that in all of these discussions about how Faraday Future “doesn’t own its intellectual property” absolutely no one seems to point out the fact that the company that everyone compares it to, Tesla, famously dumped all its patents into the public domain and told anyone to go ahead and use them. That seems like a relevant point to make in articles about this upstart competitor and its “intellectual property.” Of course, it’s possible that the articles could mean something else when it says “intellectual property” — such as trademarks — but it seems unlikely that the trademarks for a flailing company that is unlikely to ever get anything on the market are that valuable.
The whole story, and the ignoring of Tesla’s stance on patents… is just strange. It is true that sometimes failing companies hang onto their patents as a sort of last ditch effort to extract some return for their investors in a patent fire sale. But if you’ve reached that point, things have already gone way too far south to really matter. Tesla has shown that it can build a pretty damn successful company without relying on “intellectual property.” It seems that people should stop freaking out that Faraday Future may have dumped its patents into some offshore company, and focus on the company’s real problems — like the fact that its execs are racing out the door as fast as possible.
Remember that Microsoft has its own patent “assertion” (trolling) department/entity (they call it “Licensing”) and several more large companies now do something similar. Sites like IAM just call that NPEs.
“For NPEs,” (i.e. trolls) Florian Müller explained the other day, “it’s often actually desirable to make litigation more, not less, expensive. Speed and injunctive relief attract them.”
Yes, this is a truthful statement and it helps demonstrate how to mitigate/tackle the trolling epidemic if there was sufficient desire, just like limiting trolls’ movement/travel. Currently, in the Eastern District of Texas, where defendants haven’t much confidence in winning (not cheaply anyway), trolls are making a killing.
East Asia is rapidly becoming the breeding ground for the trolling epidemic, as we noted here before. The above from IAM is just one example of it, as is the IAM article titled “The signs suggest that IP monetisation activity is on the rise in Southeast Asia, says A*STAR tech transfer chief” (“IP monetisation” is a euphemism for trolling). Another new article is titled “$130 million patent claim against Apple in Shenzhen shows NPEs in China increasingly strident”. It sure looks as if SIPO has turned China into a cesspool of patent trolls. Who benefits from this? A few parasites, not ordinary Chinese people. To quote IAM, “GPNE’s Chinese assertion appears to have begun back in 2013 in the Shenzhen Intermediate People’s Court. The court’s database shows four lawsuits against Apple and associated companies at the trial stage. According to a report in China’s National Business Daily, the most recent hearing was in late November 2016; the same article also states that Apple has made three separate attempts to invalidate the asserted patent at SIPO’s Patent Reexamination Board, with all of these complaints being dismissed on appeal.”
Poor patent quality at SIPO, just like at USPTO before it, emboldens patent trolls. IAM is siding with the trolls, as usual, also in the case of Nokia against Apple — a case which it belatedly covers (Nokia has become like a patent troll which merely licenses the brand).
Writing about patent trolls in general, Wolf Greenfield & Sacks PC bemoans what happens in the US. “Over the course of the last decade,” it says, “the U.S. Supreme Court has issued a series of decisions making it more difficult for so-called non-practicing entities (NPEs)—companies that own and enforce patents but do not offer products or services covered by them—to extract value from their patents. The Court may now be ready to take a step in the other direction by removing the equitable defense of laches against patentees’ past damages claims—up to six years of damages in many cases. Oral arguments were heard in the landmark case of SCA Hygiene Products Aktiebolag v. First Quality Baby Products, LLC on November 1, 2016, and a decision is expected later this term.”
“Patent Value” for patent trolls (ignore euphemisms like “NPEs”) is also mentioned in this article. We can’t help but feel like patent law firms — not just sites like IAM (which trolls are paying) — take the side of trolls. They don’t care about innovation, just litigation. They profit from that.
United for Patent Reform, a group that battles against patent trolls, wrote the other day that “Crowdfunding company @gustly won its case over a #PatentTroll after 2 years in court.” Here is part of the statement:
The patent lawsuit filed by AlphaCap claimed ownership over “online equity financing”. As with most other patent lawsuits, the case was brought in the Eastern District of Texas. This court is known as a patent troll haven and has benefitted economically from an assumed bias in favor of trolls.
So here again we have an example where legitimate companies are hit hard by trolls that make nothing at all, just lawsuits. “Wearable device company Fitbit has moved for termination of its ITC patent complaint against Jawbone, which is unhappy at suggestions about its financial stability,” MIP wrote the other day (a move which we covered in this older post of ours). As before, Fitbit makes shameless excuses, trying to portray itself as merciful after it attacked a rival, only to realise that its case is going nowhere fast and is only wasting its own (Fitbit’s) financial resources.
Fitbit, like many other companies, must have realised that certainty of winning patent cases has gone down. Moreover, Jawbone sued Fitbit in retaliation, causing quite a big (and expensive) headache to Fitbit. As Fitbit is not a patent troll (it has actual products that it sells) it’s not hard to sue it as well, thereby compelling it to reach a ‘ceasefire’.
Meanwhile, as even IAM cares to admit, litigation numbers are down sharply and patent trolls suffer a lot:
Unified Patents and RPX have both released their early numbers on new US patent litigation cases in 2016, confirming what we have known for some time: district court cases fell dramatically, with Unified putting the total number of filings at 4,382 – a drop of 24.8% year-on-year. That is the lowest volume of new cases since 2011 when the America Invents Act (AIA) came into effect and a change in joinder rules led to an immediate increase in the number of suits. According to Unified, disputes at the Patent Trial and Appeal Board (PTAB) saw a slight drop down to 1,723 from 1,793, although last year was still the second busiest on record.
The question now is whether the 2016 litigation drop was a blip or part of a longer-term trend. The last few years have seen sharp fluctuations in the number of cases with 2013, the busiest year on record, leading into a marked fall in 2014 as plaintiffs were seemingly turned off by the Supreme Court’s Alice decision and by the prospect of patent reform. So if that is repeated, we might expect to see the number of new cases rise again this year.
MIP takes into consideration an upcoming SCOTUS case (alluded to above), but it barely bothers to mention that this case would affect trolls the most. To quote what is not behind a paywall:
Natalie Rahhal speaks to former Federal Circuit Chief Judge Paul Michel and others to assess the potential impact of In re TC Heartland at the US Supreme Court. One outcome could be a sharp fall in filing in the Eastern District of Texas and an increase in a potentially under-resourced District of Delaware
In re TC Heartland is already shaping up to be one of the most important patent cases in the US this year. The Supreme Court on December 14 granted cert in the case, which will give the court an opportunity to revisit the case law and statute governing forum selection in patent infringement suits.
We look forward to the outcome of this case because the Justices, probably well before Trump introduces new ones, are expected to serve a blow to patent trolls. Today’s Justices tend to be sceptical on issues pertaining to patents maximalism. █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
Posted in America, Patents at 3:49 pm by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
Stuff one can do with pen and paper is not an invention but a mental process

Summary: Some of the patent microcosm, or those who profit from the bureaucracy associated with patents, responds to claims made by Techrights (that software patents are a dying breed in the US)
TECHRIGHTS is not a site that patent law firms like. We are fine with that, as we never intended to be pals of those who promote patent maximalism, or those whom some dubbed the “patent microcosm” (because patents are their only ‘products’).
Yesterday we noticed that a patent lawyer had gotten sanctioned for misbehaving again (recall Andrew Y. Schroeder), based on this new (rather short) blog post from Patently-O:
From what I can tell, the lawyer was sanctioned by the district court because he settled a case, but then consistently asserted that he hadn’t; he was sanctioned on appeal for making some unsupported arguments and falsely attacking opposing counsel, it seems.
Longtime readers of ours know that we don’t have much trust and faith in the patent profession — by which we mean people who make a living purely out of patents rather than research and/or development. We don’t mean examiners (those who attempt to ensure patent quality) but those who try to convince examiners to grant every applications that they send on behalf of clients. The financial motivation of patent law firms is very much like that of companies that sell weapons and thus prefer wars or at least tension (which motivates purchases of weapons, in the name of perceived “defense”).
Mark Summerfield, writing in his blog today (in Australia where time is many hours ahead), does not agree with us (as usual) that software patents as a whole are dead and instead says that “computer-implemented business methods, including ecommerce and finance applications” — however one defines them — are in somewhat of a limbo/trouble. We mentioned this before. To quote from his conclusions:
The data presented above demonstrates that in established fields of software technology, covered by associated Art Units in USPTO Technology Center 2100, neither US court decisions nor changes in management have resulted in any identifiable deviation in US patent grant rates, despite the consistent gleeful claims of opponents that ‘software patents are dead’.
Software patents are not dead. They are here, they have been here for many years, and they are here to stay.
Computer-implemented business methods, including ecommerce and finance applications, on the other hand, are a different matter. The data clearly shows that the USPTO under Kappos was more friendly to this subject matter than under his predecessor, although the CAFC decision in Bilski appears to have forced applicants to claim machine-implementation more explicitly. However, the US Supreme Court decision in Alice looks to have eliminated about 75% of new business method patents. This implies that a similar proportion of such patents issued at least since the start of the Kappos era are invalid, which accords with the impact we have seen at the CAFC since Alice.
Whether or not patents on software get granted does not matter as much as whether or not courts deem them eligible. As we have shown here time after time the higher a case goes (up the ladder all the way up to SCOTUS), the less likely to withstand the patent/s at the centre of the case will be. We stand by our assertion that patents on software are a waste of time and money, even if the USPTO continues to grant a lot of them. Certainty around software patents is very low in the United States and it takes courages to even have them tested in a court (no out-of-court settlement or shakedown). █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
01.07.17
Posted in America, Deception, Patents at 5:03 pm by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
Nostalgic and picky/selective (as always and forever) with ‘facts’, ignoring what’s inconvenient
 Summary: Firms that are profiting from patents (without actually producing or inventing anything) want us to obsess over and think about the rare and few cases (some very old) where judges deny Alice and honour patents on software
Summary: Firms that are profiting from patents (without actually producing or inventing anything) want us to obsess over and think about the rare and few cases (some very old) where judges deny Alice and honour patents on software
SOFTWARE patents are a dying breed and thus a dying business for patent law firms. They know it, hence they’re angry and vindicative. Some of them even attack judges (the messengers). These patents keep dying both inside and outside the courtroom (e.g. PTAB) in the US, in spite of some USPTO examiners granting them, probably in an effort to inflate some numbers.
According to this patent attorney, “VA Dist. Ct. Killed 8 Wireless Patents under Alice/101: http://assets.law360news.com/0878000/878025/https-ecf-vaed-uscourts-gov-doc1-18917727618.pdf” (deemed abstract and thus ineligible).
We have not seen a single article about this case. None!
What we are seeing, on the other hand, is patent law firms’ sites romanticising/bringing up old cases, like this quick mention of McRO behind a paywall. To quote:
The full Federal Circuit has denied a bid by Electronic Arts and other gaming companies to rehear its September decision that found McRO Inc. software patents for lip-sync animation technology patent-eligible under Alice, according to an order issued by the appeals court Friday.
In other words, nothing is changing. But again, this is one among perhaps four (just 4!) decisions in the whole year when the Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit (CAFC) ruled not to invalidate a software patent. What about all the rest? What about all those patents (hundreds if not thousands) that PTAB and the courts invalidated? Shouldn’t the patent microcosm inform clients (and potential clients) of the reality?
Mishcon de Reya, the nasty and malicious firm that the EPO hired to spy on/silence Techrights, has just been quoted in relation to the same CAFC case, courtesy of a relatively new site:
Bandai Namco Games America has been denied an en banc rehearing in its cornerstone software patent case against McRO.
All regular active judges for the US Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit heard the petition and issued their response at the end of 2016.
Mark Raskin, partner at Mishcon de Reya, who is serving as trial counsel in the case, said: “We’re very excited that the entire Federal Circuit has recognised the technical innovations of our client’s inventions and the California cases will now proceed, hopefully expeditiously.”
The McRO case drew a lot of attention with its interpretation of the landmark Alice v CLS Bank decision.
As we noted before, Mishcon de Reya also works for Microsoft and the EPO. It’s hardly surprising that the firm advocates software patents. Another legal firm — one that the EPO hired to threaten Techrights — promotes the UPC.
There is another new article from a law firms’ platform, covering the Amdocs case (also at CAFC) as follows:
An interesting case came out of the Federal Circuit in Amdocs (Israel) Limited v. Openet Telecom, Inc., No. 2015-1180, 2016 WL 6440387 (Fed. Cir. Nov. 1, 2016) in which the Court reversed the district court’s granting of Openet’s motion for judgment on the pleadings on the basis that the patents were not directed to patent eligible subject matter under § 101. This is significant not for the result but for how the Court arrived at its conclusion. The majority and dissenting opinions offer several important insights: (1) the Court is struggling to find the proper “decisional mechanism” for deciding whether a software patent is directed to patent ineligible subject matter; (2) members of the Court continue to suggest borrowing from other sections of the Patent Act to analyze Section 101; and (3) claim construction can be very effective at staving off dismissal based on patent eligibility.
This ‘news’ is more than two months old. Why aren’t these legal firms covering some of the latest? Probably because it’s not convenient for them. It’s not good for their business. █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
01.05.17
Posted in America, Deception, Law, Patents at 6:19 pm by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
Producing nothing, insulting everybody
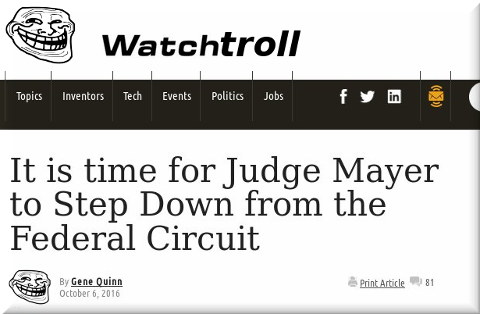
Summary: A look at some of the latest spin and the latest shaming courtesy of the patent microcosm, which behaves so poorly that one has to wonder if its objective is to alienate everyone
THE patent reform in the US (AIA, especially after Alice) brought us the blessing known as PTAB, which is responsible for the immediate and permanent elimination of many software patents and the reduction in litigation. It lowered confidence in even more of these software patents (potentially hundreds of thousands of patents).
“”Idiotic”, “impotence”… what next? Will Watchtroll accuse judges and PTAB of rape and pedophilia too?”PTAB continues to scare people who made a living from software patents (not software, just patents). With his habitual insults directed at PTAB, Gene Quinn (Watchtroll) continues to fling criticisms at PTAB, bemoaning the latest decision which he summarises with the word “idiotic” in the image (and IBM’s patent chief actually boosts these people, who also attack judges! See the image at the top!).
“Idiotic”, “impotence”… what next? Will Watchtroll accuse judges and PTAB of rape and pedophilia too? Frankly, these people are a lot more rude than anything we have ever seen and some of those people actually advertise themselves as professionals. “If a machine is patent ineligible bc it is an abstract idea,” Watchtroll wrote in Twitter, “no point in keeping powder dry. The 101 fight is now.”
He wants a “fight”.
“Telling Watchtroll about software development is an exercise in futility; he doesn’t even know how software works.”Well, the Section 101 fight is over. The patent microcosm lost. Most software patents are dying and this is good because, as Benjamin Henrion put it in his reply, “patents also destroyed software development.”
Telling Watchtroll about software development is an exercise in futility; he doesn’t even know how software works. I debated this in length with him and then he chickened out, blocking me in Twitter.
Watchtroll (a front for the patent microcosm, not just one person) is now lobbying Trump to makes Patent Chaos Again (as expected, with lots more of this lobbying to come).
“These have included enabling the PTO to attack patent validity in a second window,” says the article, “attacking classes of inventions such as software and medical diagnostics…”
“PTAB is a lot more professional because these financial incentives hardly exist, which makes their staff more objective.”Nobody is “attacking” and there is no “fight”. As we pointed out here before, the attorney known as Patent Buddy uses words like “survive”, “kill” etc. rather than use terms that don’t pertain to war. The people actually call PTAB a “death squad!” Picture that for a connotation.
Here is Patent Buddy saying about the above case: “In the MRI-101 Invalidation Decision, the PTAB Reversed the Examiner finding eligibility under 103, but not 101.”
Examiners at USPTO have historically been rewarded to just award lots of patents, irrespective of quality or prior art (which can take a long time to assemble and study). PTAB is a lot more professional because these financial incentives hardly exist, which makes their staff more objective.
Earlier this week we found this lawyers’ site claiming that “[t]he tide may be turning in the Section 101 landscape and it is making waves in the patent practice area.” No, it’s not. The patent microcosm lives in wonderland and only pays attention to a few CAFC decisions that suit their agenda. The article says that CAFC’s “latest rulings on the issue—Enfish v. Microsoft Corp., BASCOM Global Internet Services v. AT&T Mobility, and McRO v. Bandai Namco Games America—possibly signal a new direction for patent eligibility in a post-Alice era. On the damages front, the U.S. Supreme Court grabbed headlines with its highly anticipated ruling in Samsung Electronics v. Apple, the first design patent case to be examined by the Court in over a century. Our panel of experts discussed these issues as well as patent trends on the horizon in 2017.”
“There’s no “win”, it’s not a game. It’s also not a “war” or a “fight”.”We actually debunked this just recently (December 27th), in relation to similar claims about CAFC cases. Less than a handful of cases (less than one hand’s fingers) don’t change years of patent invalidations, including by Judge Mayer, whom Watchtroll is insulting (see above again).
CAFC is soon going to decide whether challenging low-quality USPTO patents (through PTAB) is acceptable, says MIP, noting about a particular case that CAFC “has granted en banc rehearing in Wi-Fi One v Broadcom. The court will consider whether judicial review is available for a patent owner to challenge the USPTO’s determination that the petitioner satisfied the timeliness requirement governing the filing of IPR petitions” (these are the petitions that typically initiate invalidation by PTAB).
Regarding this new article from lawyers’ media, one person wrote, “CAFC vs. PTAB decision discrepancies: Who wins?”
There’s no “win”, it’s not a game. It’s also not a “war” or a “fight”. In fact, most of the time CAFC agrees with PTAB, so the framing of infighting is simply incorrect and inappropriate. To quote the actual article:
Apple Inc. has won at least a moral victory in a fight with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office over touchscreen technology.
The U.S. Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit agreed with Apple on Tuesday that the patent office failed to sufficiently explain why Apple’s method for reconfiguring touchscreen icons is unpatentable due to obviousness.
Apple applied for a patent in 2009 on its method of using a sustained touch to activate an icon, which then allows a person to drag the icon to a new location on the screen. A patent examiner found the claim obvious in light of separate prior inventions on sustained touch and dragging. Combining the two inventions “would be an intuitive way” to rearrange touchscreen icons, the examiner concluded and the Patent Trial and Appeal Board affirmed.
This is just one of those exceptions where the CAFC does not fully agree with PTAB and wants the judgment reassessed.
The bottom line is, things are progressing in a positive direction as the US patent system persists in improving patent quality. It’s well overdue. Here we have a new case which “focuses primarily on §101 issues.”
“The bottom line is, things are progressing in a positive direction as the US patent system persists in improving patent quality.”To quote: “The oral argument of the week is MACROPOINT, LLC v. FOURKITES, INC., No. 2016-1286 (Fed. Cir. Dec. 8, 2016) decided by a Rule 36 judgment.”
Those who claim that Section 101 is losing its potency or that CAFC is at war with PTAB or anything like that are being extremely dishonest and typically — if not always — they are the ones directly profiting from these misconceptions/distortions.
Watchtroll and its ilk need to go away or not be taken seriously. Time after time we have demonstrated that the site’s purpose is to attack those who don’t agree (even judges!) and sometimes to organise 'echo chamber' events so as/in which to lobby officials.
Watchtroll is to the patent world what Trump is to civilised politics. █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
Posted in America, Australia, Europe, Patents at 5:27 pm by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
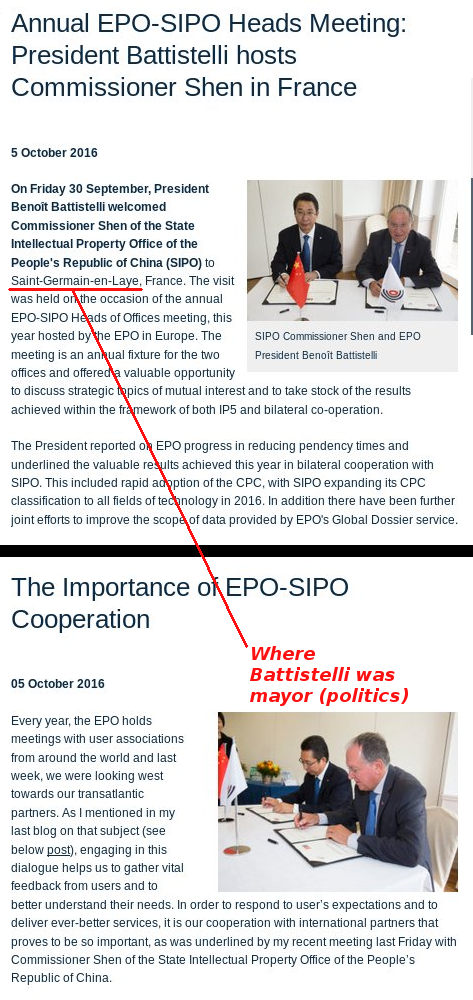
Reference: Loose Patent Scope Becoming a Publicity Nightmare for the EPO and Battistelli Does a China Outreach (Worst/Most Notorious on Patent Quality)
Summary: In defiance of common sense and everything that public officials or academics keep saying (European, Australian, American), China’s SIPO and Europe’s EPO want us to believe that when it comes to patents it’s “the more, the merrier”
RECENTLY, Australia’s Productivity Commission reiterated its opposition to software patents (as before), only to face protests from the patent microcosm (also as before). The report came out so close to Christmas that not many people covered it. During the holiday TechDirt wrote that:
Back in May we were both surprised and delighted by a thorough and detailed report from the Australian Productivity Commission noting that copyright was broken and harming the public, and that it needed to be fixed — with a core focus on adding fair use (which does not exist in Australia). It similarly found major problems with the patent system. It was a pretty amazing document, full of careful, detailed analysis of the problems of both the copyright and patent systems — the kinds of things we discuss all the time around here.
TechDirt focused on copyright aspects of the output from Australia’s Productivity Commission. We already wrote about half a dozen posts about the patent aspects of the Productivity Commission’s report (May and December). The bottom line is, the Productivity Commission basically bemoans both copyright maximalism* and patent maximalism; it specifically chastises software patents. These are seen as detrimental to Australia (rightly so!).
“The bottom line is, the Productivity Commission basically bemoans both copyright maximalism and patent maximalism; it specifically chastises software patents”Look at China for a cautionary tale. It’s quickly becoming a terrible place for inventors and producers to be in. “Patent inventorship has been disputed in several recent cases in China. Wenhui Zhang reviews four court decisions that provide lessons for inventors,” MIP writes. China’s patent office, SIPO, has become the dumpster of rejected patents — the place where one is guaranteed little scrutiny and lots of cheap patents (expensive in a court where the lawyers can make a killing). The EPO is going down the same route under Battistelli, although this transition is a gradual one.
“Right now it’s risky to even look at successful applications because that leads to higher liability/damages in case of infringement.”In a later post we are going to show just how quickly patent trolls are emerging in China as a result of SIPO’s policies. It’s quite incredible, especially in light of the death of patent trolls in the US (due to patent scope restrictions, among other restrictions).
Remember how the patent system was originally, as per the history books, conceived as a way to reward inventors and for publication of inventions? Not anymore. Right now it’s risky to even look at successful applications because that leads to higher liability/damages in case of infringement. And watch what MIP is currently saying about PCT. “For many patent applicants,” it says, “the primary value of the PCT is as a delaying tactic.”
Great for productivity, eh? Not.
“As a reminder, China is now (officially!) perfectly okay even with patents on software and business methods.”“With prosecution costs being a significant contributor to the total price of obtaining patent protection,” MIP says, “applicants are well advised to make strategic decisions early on in the application process to limit costs further down the line. International (PCT) applications are known by many applicants and IP professionals as a convenient delaying tactic when considering jurisdictions in which to file applications following a first filing.”
More than half a decade ago we wrote many articles about the dangerous vision of a global (or globalised) patent system and what it would entail. Now, imagine those million plus patent applications in China (obviously low quality patents) being pointed at every single country/company in the world. As a reminder, China is now (officially!) perfectly okay even with patents on software and business methods. █
________
* The misguided idea that copyright scope, rigidness, lifetime etc. should be maximal if not infinite. This tends to promote centralisation of power/ownership, monopolisation, and harm to culture, curation, preservation, free expression, etc.
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
01.03.17
Posted in America, Asia, Europe, Patents at 10:45 am by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
EPs are becoming ever more useless (hence a waste of money) under Battistelli

Summary: To nobody’s surprise, the past half a decade saw accelerating demise in quality of European Patents (EPs) and it is the fault of Battistelli’s notorious policies
THE overpaid ‘king’ of the EPO (who keeps the salary he is giving to himself secret, like in a third world country) keeps rewarding himself and his protectors for leading the Office in a self-destructive path — a lethal trajectory that would leave nobody but them (the top-level management) well off financially. The have the economic tenacity of oligarchs that prey on states for profit. They need to be stopped before it’s too late (if it’s not too late already, as redundancies loom over the horizon).
Earlier this afternoon an article from Heise’s Christian Kirsch was published in German. An automated translation of the article tells us it’s much of the old stuff, i.e. not much new information. “Proceedings before the ILO may take up to ten years,” explains Kirsch and also “there are different opinions between the employees and Battistelli about the “improvement in productivity” that he has advanced in the EPO.” To quote the automated and unedited translation: “Visible the first time in 2011. At that time, were the President suggested that the employees from the surplus of the Office a bonus of 4,000 euros net pay. On the other hand, the employees’ representatives expressed their opinion: such a bonus signals that the goal is above all to grant many patents and consequently to generate a high fee. It is, however, essential to examine the applications thoroughly and to maintain the high standard of the EPO in the granting of patents.”
IP Kat‘s debunking of patent quality claims is cited also. To quote: “Auditors and patent attorneys, however, are skeptical about what Battistelli’s “productivity increase” is about, which should have amounted to about 14 percent in 2015. To interpret the figures according to the British Blogs IPKat considers out that the Office has resorted to “cherry-picking”…”
A lot of the rest deals with the spineless [cref 96056& chinchillas] of the Administrative Council, the attack on the independence of the appeal boards, attacks on SUEPO, and at the very end Brexit’s effect on the UPC (the automated translation there is too mangled to be comprehensible).
Looking across the Atlantic at the USPTO, things appear to have meanwhile improved. As Patently-O said after the new year had begun, patents continue to be challenged by PTAB, which is sort of an equivalent of the appeal boards in the EPO (though not exactly similar). One new article says about claims of temporal separation between two communications in a patent that a court stepped in and:
On remand, the PTAB will decide whether the prior art the claim elements as they are more narrowly defined.
Remember that PTAB did not even exist more than half a decade ago!
Battistelli’s vision of the EPO is akin to that of a registration office with minimal appeal opportunities. Because hey, who needs justice anyway? It’s not as though today’s EPO cares about justice. Not even of its own employees…
Another new article of Patently-O says:
The Supreme Court has in recent years routinely rejected the Federal Circuit’s rigid, cabined interpretations of the Patent Act. While no one knows what the future holds, today’s practitioner’s conduct may be judged by a more stringent standard than suggested in Therasense and proposed here. That has happened with eligibility, obviously. Given that the Supreme Court could hold that the Patent Act requires more than avoiding intentionally obtaining a patent that you know you shouldn’t get, and given that that interpretation will likely be applied to all issued patents, and given the USPTO’s statement that it hopes that the new definition will result in less disclosure, one can see a trap for the unwary practitioner. This may give practitioners a false sense of security.
By “practitioners” he means the patent microcosm, or the bunch of people who profit from patent maximalism without actually producing anything (other than paperwork).
And speaking of patent scope, today IAM correctly points out that China has become the land of patent chaos. Patent quality barely exists there and Battistelli seems to be emulating that. He wants a production/assembly line, not a patent office. It’s far too easy to just grant a patent on every piece of garbage and figment of imagination; it’s a lot harder to come up with real inventions and ensure that these — and these alone — get granted a patent, making a European Patent (EP) synonymous with somewhat of a trophy. Here is what IAM (patent maximalists) wrote:
Pro-plaintiff China – Not only does China handle more patent applications than anywhere else on earth, as well as more patent suits, but it is now also becoming one of the world’s most patent-friendly jurisdictions. This was a trend that accelerated during 2016, when it emerged that the Beijing IP court – one of three established in the country in 2014 (the others being in Shanghai and Guangzhou) – had handed foreign rights owners a 100% win rate in its first full year of operation. What’s more, unlike their counterparts in the US, the Chinese courts are willing and able to hand out injunctions, as the likes of Samsung and Apple discovered last year. Not everything in China’s patent garden is rosy – damages are low (though getting higher), enforcement of court decisions is often a problem and there are issues around protectionism – but for a country that has no strong patent tradition, China has come a long way very fast. And with manufacturing jobs moving to lower cost countries, the government’s push for an economy built on innovation is only likely to reinforce this trend. Perhaps the most significant confirmation of what is happening came at the end of the year when it was announced that Qualcomm had settled a high-stakes patent dispute with mobile manufacturer Meizu. This was an American company that had taken action against a flag-waving local business and, in the end, the latter concluded it could not win. That says a lot.
Speaking of China, Tian Lu reviews a book of Qiao Yongzhong. “Many experts in China, including Dr. Qiao,” Lu explains, “feel no smugness with the huge patent filing numbers.”
It’s just a big heap of garbage. The EPO seems to be heading in the same direction, unlike the USPTO, owing in part to SCOTUS with the above-mentioned rulings.
For Europe to be competitive we must ensure that European authorities recognise the colossal damage Battistelli is causing and belatedly step in. █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
12.30.16
Posted in America, Asia, Patents at 2:42 pm by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
South Korea typically finds a healthy balance on patents, from which the country benefits (economy and innovation)

Seoul Plaza, South Korea
Summary: An outline of recent stories about patents, where patent quality is key, reflecting upon the population’s interests rather than the interests of few very powerful corporations
THE NEW YEAR IS ABOUT to start and we are eager to see governments all across the world recognising that patents have gone too far if examiners are granting millions of them. Techrights was never an anti-patent site; rather, it was pro-patent quality. We need to limit patent scope so as to ensure that the practical (or economic) impact of patents benefits society at large. The former Chief Economist of the EPO spoke about it earlier this winter.
“We need to limit patent scope so as to ensure that the practical (or economic) impact of patents benefits society at large.”Florian Müller has this new article about a Korean antitrust ruling. We have been writing about rulings of this kind for nearly a decade (going back to the Korean ruling on monopolistic Intel) and 3 months ago we wrote about Microsoft's latest patents controversy in Korea. We remind readers that Korea’s official position is that software is not patentable (different from Japan’s and China’s policy).
“I wish to point out,” Müller wrote, “that ACT is generally very IPR owner-friendly, but when it comes to FRAND licensing of standard-essential patents, its positions are pretty consistent with mine. An organization that takes similar positions on FRAND (and of which Google is a member) is the Brussels-based Fair Standards Alliance. Presumably the reason the FSA hasn’t spoken out on the Korean ruling yet is simply that people in Brussels tend to be on vacation this week (to a far greater extent than in the U.S.).”
“For the record, Florian Müller assured me he had been in no way associated with (or paid by) Microsoft for several years now.”As we noted earlier this year, the Fair Standards Alliance is rather mysterious, but the same cannot be said about ACT. I politely told Müller it’s worth pointing out that Association for Competitive Technology (ACT) is a Microsoft front group with decades of history (going back to the nineties, under another name and acronym). We have exchanged some messages about that [1, 2, 3, 4]. For the record, Florian Müller assured me he had been in no way associated with (or paid by) Microsoft for several years now. A lot of what we wrote about Florian Müller is no longer relevant/applicable as he left behind his Microsoft work and has no intention to do that again. Some people will never forgive him for that, but I have. I believe that he’s not “up for sale” now that he leads a team of “app” developers, hence not dependent on contracts from companies like Oracle, either.
“Just updated post on antitrust ruling against Qualcomm with link to unofficial translation of KFTC press release,” he added, after he mostly focused on ACT’s message. Here is a report we found about the news earlier this week:
A South Korean regulator said it would fine Qualcomm Inc. about $853 million for alleged antitrust violations, the highest such penalty handed to an individual company here, as the U.S. chip maker faces global scrutiny over its patent-licensing business.
A lot of people later discussed the relevance of this to the situation in China, where Qualcomm’s shakedown efforts have only met very limited success.
The Reinhold Cohn Group, writing this new article (“China may become more liberal towards business method and software related patents”), reminds us that China has gone bonkers with patent scope. SIPO now copies/emulates the mistakes of the USPTO and it already becomes a patent trolls’ heaven. It’s beneficial to nobody. “On 27 October 2016,” as the law firm put it, “the State Intellectual Property Office of China (SIPO) published, for comments by the public, proposed draft revisions to its current Examination Guidelines for examining software-related inventions. In the draft revised Guidelines SIPO goes one step further, as, in addition to granting patents on software-related inventions that solve a technical problem, is willing to allow patents for data carriers, and, in some cases, even for business methods.”
“SIPO now copies/emulates the mistakes of the USPTO and it already becomes a patent trolls’ heaven.”So basically they want to be the garbage dump of failed patent applications, or the equivalent of scholarly journals that almost blindly accept every submitted paper (and are hence worthless and have no following). We are gratified to see the USPTO departing from this lunacy left (having been accentuated) by David Kappos. Incidentally, some LLC (usually trolls) turns out to have sued the USPTO for last year’s long outage; it has just lost the case*.
Jasper L. Tran, writing in the Iowa Law Review, has just published “Abstracting About “Abstract Idea”” — a short paper in which he tackles the classification of some patents as “abstract”. Also today, an article titled “Software patent eligibility in Canada: IP year in review” was published but then deleted, maybe by accident. █
__________
* To quote Pharma Patents Blog: “On December 2, 2016, Judge O’Grady of the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of Virginia granted the USPTO’s motion to dismiss the complaint brought by Elm 3DS Innovations, LLC over the “holidays” declared December 22-24, 2015 when the USPTO experienced a power outage that impacted its electronic filing systems. The decision may leave other stakeholders wondering whether Elm was not the best party to challenge the USPTO’s action, or whether the action is simply unreviewable under the APA.”
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
12.29.16
Posted in America, Deception, IBM, Patents at 7:53 pm by Dr. Roy Schestowitz
They even organise events to push their agenda

Summary: The latest facts and figures about software patents, compared to the spinmeisters’ creed which they profit from (because they are in the litigation business)
“L
atest [Section] 101 Statistics Show Improved Validity Prospects at Dist. Cts, Not CAFC or PTAB,” said a patent attorney the other day, reinforcing our response to Mullin's article (titled “These three 2016 [CAFC] cases gave new life to software patents”). The reality in the US right now is undeniably bad for software patents, which are being chopped at PTAB’s block and CAFC’s block. Patent maximalists are trying to pretend otherwise and we repeatedly rebut their arguments, only to see these arguments resurfacing over and over again, courtesy of the usual suspects. If the lies are repeated often enough, then maybe prospective applicants (or clients in need of legal representation) will actually believe them.
“The reality in the US right now is undeniably bad for software patents, which are being chopped at PTAB’s block and CAFC’s block.”The other day we saw this new article titled “Assessing USPTO’s Memo On Software Claim Patent Eligibility”; we keep wondering if USPTO officials will become as rational and realistic as US courts. Right now they just strive to rubberstamp whatever they can and those who pay the price for it are both plaintiffs and defendants; only patent law firms profit from it.
“This method of presentation involves storing and processing applications or parts of applications at a user’s local personal computer rather than at a remote server.”
–PatentDocsAs a side note — although an important note nonetheless — we can’t help but notice that IBM keeps trying to corrupt the system though its former Director, who had worked for IBM beforehand. IBM definitely used to be a (GNU/)Linux friend. Now it’s just an Apple promoter/pusher and a malicious patent aggressor. Yes, IBM has been rather busy going after small companies using software patents. Some of these companies, seeing what a menace IBM is becoming, belatedly turn to PTAB in an effort to invalidate these patents of IBM. Here is one report about IBM’s software patent that will quite likely be invalidated: “The ’967 patent relates to a method for presenting applications in an interactive service featuring steps for generating screen displays of the service applications at the reception systems of the respective users. This method of presentation involves storing and processing applications or parts of applications at a user’s local personal computer rather than at a remote server. This helps avoid possible server bandwidth issues that can be caused by the server being required to serve too much data to multiple users simultaneously. The ’967 patent lists many applications that can take advantage of this method of presentation, including games, news, weather, movie reviews, banking, investments, home shopping, messaging, and advertising.”
This is pretty trivial. It’s akin to caching.
Now watch what David Kappos is cited as saying again. “US is losing the innovation war,” he is quoted by IBM as saying, “to China” (where IBM finds buyers for its failing business units, notably Lenovo).
“Kappos is a paid lobbyist,” Benjamin Henrion noted, “working for patent trolls such as Microsoft or IBM.”
“IBM’s Schecter would know,” I replied, as “he’s IBM’s patent chief ^_^ so [he] has the ‘receipts’…”
What we have here is IBM citing as ‘proof’ a former IBM staff who is now an IBM-funded lobbyist for software patents. Look how dirty (as in dirty play) these people are…
And as if the greater the number of patents, the better… who would be foolish enough to actually believe this?!
“China pushing for software patents,” Henrion noted in relation to another Schecter tweet, “apparatus claims relating to software can contain both hardware and “program” components…” (links to “China Files A Million Patents In A Year, As Government Plans To Increase Patentability Of Software”)
“Kappos is a paid lobbyist working for patent trolls such as Microsoft or IBM…”
–Benjamin HenrionChina is their new bogeyman. One of these people added: “But USA keeps working on UN-patentability of software. What’s wrong with this picture?”
Nothing is wrong with this picture. It’s a good decision. End software patents, end patent trolls.
“China is plain wrong on this,” Henrion wrote, separately noting (to Marietje Schaake regarding software patents in Europe) that it’s “like the unitary patent lie that it won’t affect software development.”
On a final note, worth seeing is this rant from Watchtroll and 'gang' about end of software patenting (or demise thereof). “Stepping Back from the Cliff: The Year Congress Didn’t Cave to the Anti-Patent Lobby” says the title. They’re currently taking stock of a terrible year for them [1, 2] — a year which saw the demise of patent trolls. Watchtroll continues to attack PTAB for doing its job and we can’t help wondering why IBM’s Schecter treats this like some kind of ambassador for his cause. Does IBM really want to be so closely associated with Watchtroll, who even resorts to attacking judges?
For a more balanced summary of recent events, see “Year in Review: The Top-Five Legal Developments of 2016″ (posted days ago). It has a section about software patents.
“…anti patent trolling would be better, even if trolling is considered pejorative.”
–Benjamin HenrionThose who are against software patents, notably people who actually write software, are not “anti-patent” as Watchtroll tries to put it. In fact, as Henrion put it, “anti-patent is a gross and blunt exaggeration here. […] anti patent trolling would be better, even if trolling is considered pejorative.”
Patent trolls, in the majority of cases, rely on software patents. Take the latter away to get rid of the former. █
Permalink
 Send this to a friend
Send this to a friend
« Previous entries Next Page » Next Page »



 Summary: Firms that are profiting from patents (without actually producing or inventing anything) want us to obsess over and think about the rare and few cases (some very old) where judges deny Alice and honour patents on software
Summary: Firms that are profiting from patents (without actually producing or inventing anything) want us to obsess over and think about the rare and few cases (some very old) where judges deny Alice and honour patents on software




















 Content is available under CC-BY-SA
Content is available under CC-BY-SA